
Earthen works surrounding the Confederate battery atop Saint John’s Bluff along the Saint John’s River in Florida, 1862 (J. H. Schell, public domain).
Following their early October 1862 routing of Confederate States Army troops at an artillery battery on Saint John’s Bluff in Duval County, Florida—a battery which had been strategically positioned to prevent Union ships from making their way from the Atlantic Ocean and mouth of the Saint John’s River at Jacksonville to Palatka and points south, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers joined other Union soldiers in disabling the battery. According to 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantryman Henry D. Wharton:
“On the day following our occupation of these works the guns were dismounted and removed on board the steamer Neptune, together with the shot and shell, and removed to Hilton Head. The powder was all used in destroying the batteries.”
Meanwhile that same weekend (Friday and Saturday, October 3-4, 1862), Brigadier-General John Milton Brannan, who was quartered on board the Ben Deford as the Union expedition’s commanding officer, Colonel Tilghman H. Good, commanding officer of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers, and other Union officers serving under Brannan were busy penning reports to their respective superiors, and were also planning their next move to further secure this region of Florida, which had been deemed of key strategic importance by senior Union military leaders due to the significant role the state had been playing as a supplier of food to the Confederacy.
On Saturday, Brannan chose several officers to direct their subordinates to prepare rations and ammunition for a new expedition that would take them roughly 20 miles upriver to Jacksonville. (A sophisticated hub of cultural and commercial activities with a racially diverse population of roughly 2,100 residents, the city had repeatedly changed hands between the Union and Confederacy until its occupation by Union forces on March 12, 1862.) Among the Union soldiers selected for this mission were 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers from Company C, Company E, and Company K.

Provost Marshal’s guardhouse, Jacksonville, Florida, 1864 (public domain).
One of the first groups to depart—Company C of the 47th Pennsylvania, did so that Saturday as part of a small force made up of infantry and gunboats, the latter of which were commanded by Captain Charles E. Steedman. Their mission was to destroy all enemy boats they encountered to stop the movement of Confederate troops throughout the region. Upon arrival in Jacksonville later that same day, the infantrymen were charged by Brannan with setting fire to the office of that city’s Southern Rights newspaper.

This special pro-Union edition of Jacksonville, Florida’s formerly pro-Confederate Southern Rights newspaper was written and printed by Henry Wharton and other members of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers on October 4, 1862 (public domain).
Before that action was taken, however, Captain John Peter Shindel Gobin and his subordinate, Henry Wharton, who had both been employed by the Sunbury American newspaper in Sunbury, Pennsylvania prior to the war, salvaged the pro-Confederacy publication’s printing press so that Wharton could more efficiently produce the regimental newspaper he had launched while the 47th Pennsylvania was stationed at Fort Taylor in Key West, Florida. That salvage operation also gave Wharton and several of his C Company comrades the opportunity to take a parting, verbal “shot” at Confederate sympathizers in the region by publishing a snarky, final edition of the paper. Dated October 4, 1862, its text included the following:
“On account of the presence of distinguished visitors, the election is indefinitely postponed.
A few lines have been taken from the matter of this page to make room for explanation.
The form from which we strike off a few copies, is the same taken from Secession Printing Office at Jacksonville, Fla., on the expedition of Gen. J.M. Brannan to the St. John’s River.
Wishing to know whether secesh type would print under Federal rule, we concluded to bring along with us the press and fixtures; to our surprise and gratification we find the machine prints almost alone, satisfying us that it rejoices at the change. We have no doubt it will continue the good spirit already manifested and will make itself generally useful under the kind treatment already received, in printing various blanks required by the Post. It is possible it may get patriotic and issue a Constitutional Union Paper.
Beaufort, S.C. Oct. 17, 1862
Notice
The editor of this paper is absent from town for a few days on urgent business in the interior. It is therefore announced that the publication of this Paper will hereafter be weekly suspended as it has been heretofore, weakly continued.
The taking of our battery after a loss of courage, but no blood, and the presence of the yankee [sic] fleet, and the fearful proximity of Gen. Brannan and his forces, render the Southern Rights precarious.
The friends of Col. Hopkins are informed that the Colonel declines to run as a candidate for the office of Senator, notwithstanding the good time he made running from St. John’s Bluff.”
According to historian Lewis Schmidt, the “newspaper contained other original articles of local interest,” as well as the announcement of a $25 reward for the capture of Ned, a 28-year-old Black man who had escaped slavery near Jacksonville.
On Sunday, October 5, Brannan and his detachment sailed away for Jacksonville at 6:30 a.m. Per Wharton, the weekend’s events unfolded as follows:
“As soon as we had got possession of the Bluff, Capt. STEEDMAN and his gunboats went to Jacksonville for the purpose of destroying all boats and intercepting the passage of the rebel troops across the river, and on the 5th Gen. BRANNAN also went up to Jacksonville in the steamer Ben Deford, with a force of 785 infantry, and occupied the town. On either side of the river were considerable crops of grain, which would have been destroyed or removed, but this was found impracticable for want of means of transportation. At Yellow Bluff we found that the rebels had a position in readiness to secure seven heavy guns, which they appeared to have lately evacuated, Jacksonville we found to be nearly deserted, there being only a few old men, women, and children in the town, soon after our arrival, however, while establishing our picket line, a few cavalry appeared on the outskirts, but they quickly left again. The few inhabitants were in a wretched condition, almost destitute of food, and Gen. BRANNAN, at their request, brought a large number up to Hilton Head to save them from starvation, together with 276 negroes—men, women, and children, who had sought our protection.”
* Note: Yellow Bluff, which was situated five miles to the north of Saint John’s Bluff on the opposite side of the Saint John’s River, was the site of another Confederate artillery battery—one surrounded by T-shaped earthen works that had been erected earlier in 1862.
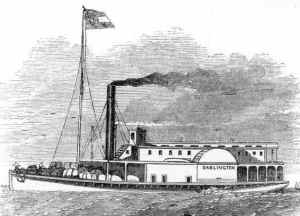
The Darlington, a former Confederate steamer turned Union gunboat (public domain).
Receiving word soon after his arrival at Jacksonville that “Rebel steamers were secreted in the creeks up the river,” Brigadier-General Brannan ordered Captain Charles Yard of the 47th Pennsylvania’s Company E to take a detachment of 100 men from his own company and those of the 47th’s Company K, and board the steamer Darlington “with two 24-pounder light howitzers and a crew of 25 men.” All would be under the command of Lt. Williams of the U.S. Navy, who would command the “convoy of gunboats to cut them out.” Describing the Darlington in a subsequent diary entry, Corporal George R. Nichols of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers’ E Company wrote:
“This steamer is runn [sic] by a negro crew and this same crew runn [sic] her away from the Rebels out of charleston [sic] harbor Passed [sic] forts Sumpter and Moltre [sic] and all the land Batterys [sic] and turned her over to Uncle Sam. The crew is Brave and Smart and that if they are Black men.”

The rebel steamer Governor Milton, captured by the U.S. flotilla in St. John’s River, Florida (Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper, courtesy: State Archives of Florida, Florida Memory Project, public domain).
According to Schmidt, the small force steamed upriver roughly 100 to 200 miles “to Lake Beresford, where they then assisted in capturing the [68-ton] steamer Governor Milton,” which had been renamed in honor of Florida’s governor after having been “formerly known as the George M. Bird [under its previous owners] a New England family named ‘Swift’, who were timber cutters and used it as a tug boat to tow rafts loaded with live oak to the lumber market.”
Corporal Nichols of E Company went on to describe the capture as follows:
“At 9 PM … October 7, discovered the steamer Gov. Milton in a small creek, 2 miles above Hawkinsville; boarded her in a small boat, and found that she had been run in there but a short time before, as her fires were not yet out. Her engineer and mate, then in charge, were asleep on board at the time of her capture. They informed us that owing to the weakness of the steamer’s boiler we found her where we did. We returned our prize the next day…..
I commanded one of the Small Boats that whent [sic] in after her. I was Boatman and gave orders when the headman jumped on Bord [sic] take the Painter with him. That however belongs to Wm. Adams or Jacob Kerkendall [sic]. It was So dark I could not tell witch [sic] Struck the deck first. But when I Struck the deck I demanded the Surrend [sic] of the Boat in the name of the U.S. after we had the boat an offercier [sic] off the Paul Jones, a Gun Boat was with us he ask me how Soon could I move her out in the Stream I said five minuts [sic]. So an Engineer one of coulered [sic] Men helped me. and I will Say right hear [sic] he learned Me More than I ever knowed about Engineering. Where we Started down the River we was one hundred and twenty five miles up the river. When we Stopped at Polatkey [Palatka] to get wood for the Steamer I whent [sic] out and Borrowed a half of a deer that hung up in a cut house and a bee hive for some honey for the Boys. I never forget the boys.’”
According to Brigadier-General Brannan, the Union party “returned on the morning of the 9th with a Rebel steamer, Governor Milton, which they captured in a creek about 230 miles up the river and about 27 miles north [and slightly west] from the town of Enterprise. Lt. Bacon, my aide-de-camp, accompanied the expedition… On the return of the successful expedition after the Rebel steamers… I proceeded with that portion of my command to St. John’s Bluff, awaiting the return of the Boston.”
This return trip did not happen without complications, however; in a letter penned to The New York Times on October 14, Wharton reported the following:
“Finding that the Cosmopolitan, which had been sent to Hilton Head for provisions, had struck heavily in crossing the bar, on her return to the St. John’s River, and was temporarily disabled for service, the Seventh Connecticut Regiment was sent to Hilton Head on the Boston, with the request that she should return for the remainder of the troops, and she got back on the 11th, when the command was reembarked, reaching this plane yesterday, excepting one company of the Forty-seventh Pennsylvania, which is left for the protection of the Cosmopolitan. The accident to this valuable steamer is severe. A large hole was made in her bottom and she filled, but she will not be a wreck, as was at first feared.”
The Governor Milton, which would later be appraised by the Union Navy at $2,000, was also temporarily left behind, under the command of Captain Steedman so that its boiler could be repaired. Overseeing those repairs was Corporal Nichols, who had been temporarily detached from the 47th Pennsylvania’s E Company. Observed Nichols:
“So hear [sic] we are at Jacksonville and off we go down the river again, and the Captain Yard Said you are detailed on detached duty as Engineer well that beats hell. I told him I did not Enlist for an Engineer. well I cannot help it he said. I got orders for you to stay hear [sic]. When the Boys was gone about a week orders came for us to come to Beaufort, S. Carolina by the inland rout over the Museley Mash Rout. So I Borrowed a twelve pound gun with amanition [sic] for to Protect our Selves with. But I only used it once to clear Some cavelry [sic] away. We Passed fort Palask [sic]. But that was in our Possession and we got Back to Beaufort all right. and I whent [sic] up to See the Boys and Beged [sic] captain to get me Back in the company, But he could not make it go.”
Integration of the Regiment
Meanwhile, as those activities were unfolding at Saint John’s Bluff, Yellow Bluff, Jacksonville and aboard the Governor Milton, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry was making history back in South Carolina when it became an integrated regiment on Sunday, October 5, 1862—three months before President Abraham Lincoln officially issued the Emancipation Proclamation.

Roster entries for Privates Abraham and Edward Jassum confirm their October 1862 enlistments with Company F, 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry in Beaufort, South Carolina (Registers of Pennsylvania Volunteers, Pennsylvania State Archives, public domain).
On that day, two Black men who had been freed from slavery in Beaufort, South Carolina—Abraham Jassum and Bristor Gethers—enlisted with the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers at a recruiting depot in Beaufort.
Jassum, who was just 16 years old, mustered in as a “negro undercook” with Company F. Military records described him as being 5 feet 6 inches tall with black hair, black eyes and a black complexion, and stated that his occupation prior to enlistment was “Cook.” (Those same records also confirm that Abraham Jassum continued to serve with F Company until he honorably mustered out at Charleston, South Carolina on October 4, 1865 when his three-year term of enlistment expired while an alternate set of records offers an alternate date of October 16, 1862 for his enlistment.)

Possible name variants for Bristor Gethers of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers, 1894 (U.S. Civil War General Pension Index Cards, U.S. National Archives, public domain).
Gethers, a 33-year-old man whose name was misspelled repeatedly on military records throughout and following his enlistment tenure (as “Presto Gettes” on his muster roll entry and later listing in the Civil War Veterans’ Card File in the Pennsylvania State Archives and as “Presto Garris” and “Bristor Geddes” on U.S. Civil War Pension records), also mustered in with Company F as a “negro undercook.” Described on military records as being 5 feet 5 inches tall with black hair, black eyes and a black complexion, his entry in the Civil War Veterans’ Card File noted, perhaps incorrectly, that he had been employed as a fireman. (These same records also indicate that Bristor Gethers honorably mustered out at Charleston, South Carolina on October 4, 1865 upon expiration of his three-year term of service while federal records indicate that he and his wife, “Rachel Gethers,” applied for his Civil War Pension from South Carolina.)
The regiment’s integration also continued mid-month with the October 15 enlistment of 22-year-old Edward Jassum, who was also initially assigned to Company F as an undercook. (These same records indicate that he was transferred two years later—to Company H—on October 11, 1864, and that he also continued to serve with the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers until being honorably discharged on October 14, 1865 upon expiration of his three-year term of service.)
Mop Up and Return to Headquarters
As that integration of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry was taking place in Beaufort, South Carolina, Brigadier-General Brannan’s expeditionary force was winding down its activities in Duval County, Florida. According to a letter penned by Private William Brecht of the 47th Pennsylvania’s K Company, once the artillery pieces were carried away from Saint John’s Bluff by Brannan’s troops, Brannan ordered Captain Henry D. Woodruff of the 47th’s D Company to take his company as well men from Company F and Company I to “blow up the fort, which was done with the most terrific explosions, filling the air for a great distance with fragments of timber and sand.”
“And thus came to an end Fort Finnegan, on St. John’s Bluff,” mused Brecht, who added that “after we destroyed the fort and it exploded into the air, the steamer Cosmopolitan which had been damaged and was full of water, we pumped out and fixed up again.”
Recapping the activities of his troops for his superiors, Brannan subsequently stated that, on Saturday, October 11:
“I embarked the section of the 1st Connecticut Battery, with their guns, horses, &c., and one company of the 47th on board the steamer Darlington, sending them to Hilton Head via Fernandina, Fla…. [T]he Boston having returned, I embarked myself, with the last remaining portion of my command, except one company of the 47th left to assist and protect the Cosmopolitan…which was stuck on the bar…for Hilton Head, S.C., on the 12th instant, and arrived at that place on the 13th instant. The captured steamer Governor Milton I left in charge of Capt. Steedman, U.S. Navy and Cpl. Nichols.”
According to Schmidt:
“Company F embarked for Hilton Head on Friday and arrived home on Sunday, while Company D embarked on Saturday…but did not leave the St. John’s River til Sunday…. Some of the troops, including Company C, had returned to Beaufort on Saturday, October 11, but at least portions of Company K did not return until the following Tuesday. Returning with Company C was Capt. Gobin, who had contracted intermittent fever during the expedition and was hospitalized as soon as he returned….
Company D arrived back at Hilton Head on Saturday, and Company B and F on Sunday; and by Monday, October 13, most of the troops were back in camp in Beaufort, including Companies, A, G and K which arrived on this date. Company E did not arrive until Wednesday and Company H on Thursday night.”
Although Corporal Nichols of E Company would not return from his detached duties aboard the Governor Milton until much later, Captain Gobin was able to return to active duty on October 20. Crediting his recovery to “good nursing and an abundance of quinine,” he resumed leadership of the 47th Pennsylvania’s C Company, which had returned to South Carolina nine days earlier.
October 20 also proved to be an important day for the regiment when The New York Times published a letter that had been penned six days earlier by Wharton, and which recapped the events of the St. John’s Bluff Expedition and subsequent successes by Brigadier-General Brannan’s troops. In addition to excerpts presented above in this article and in the article, “Late September to Early October 1862: First Victory,” Wharton’s letter also included the following insights:
“Gen. BRANNAN thinks it evident, from his experience on this expedition, that the rebel troops in this portion of the country have not sufficient organization and determination, in consequence of their living in separate and distinct companies, to sustain any position, but seem rather to devote themselves to a system of guerrilla warfare. This was exemplified by the advance on St. John’s Bluff, where, after evacuating the fort, they continued to hover on our flanks and front, but did not come near enough to make their fire effective. We learned at Jacksonville that they commenced evacuating the Bluff immediately after our surprise of their pickets at Mount Pleasant Creek.

Major-General Ormsby M. Mitchel, Commanding Officer, U.S. Department of the South, circa 1862 (public domain).
Wharton also included remarkable details regarding the October 12, 1862 dedication of the First African Baptist Church on Hilton Head Island, South Carolina by Union Major-General Ormsby Mitchel—during which Mitchel outlined his plans for the creation of Mitchelville—“the first self-governed town of formerly enslaved people in the United States,” according to staff at the Historic Mitchelville Freedom Park. Wharton observed that:
“On Sunday the negro church at Hilton Head was dedicated to Divine service. Gen. HUNTER authorized the construction of the building, and before he left the work was nearly finished. The situation of the church is good; the appearance is neat, though plain as a Quaker meeting-house, and in all respects the building meets the requirements of the case. Three hundred persons may be comfortably seated. The Pastor is a black man from Savannah, named ABRAM MURCHISON, who has been in due form ordained a Baptist minister by the army Chaplains, and installed in office. ABRAM, though able to read and write, is not polished in his manners; but what he lacks in culture is more than compensated in earnest eloquence, a vigorous and clear expression of his views, deep piety, and a powerful influence over the colored people. The dedication exercises were interesting in themselves, being conducted by Rev. H.N. HUDSON, Chaplain of the New-York Volunteer Engineer Regiment, and elocutionist of celebrity. Gen. MITCHEL was present, with the members of this Staff, and, by invitation, addressed the audience. His remarks were pointed, impressive and instructive. They were listened to attentively, and indorsed [sic] with nods of approbation from young and old. I do not think that a portion of the TIMES could be better filled than with this frank and unmistakable expression of the Gen. MITCHEL’s views on the negro question. He said:
‘I have been requested to say a few words to you by your teacher, who is a good man. Any good man I like, regardless of color. I respect him as much whether he is black or white. If he be a bad man I shall treat him as such, whether he is white or black. Most of you know that I have talked to all my soldiers since I came here, and now I am talking to you who are another set of soldiers, who have not yet arms in their hands, but are under my protection and guidance, and in whom I take interest. With your past life I fully sympathize. I know and understand it all. I was reared in the midst of Slavery, born in Kentucky, and know all about it. While there are many things connected with it that are pleasant, to which you will testify, there are a vast many other things which are not pleasant, and I think that God intends all men shall be free, because he intends that all men shall serve him with their whole heart. I think this is true. I am not certain. I don’t know. But in any condition we can all love and serve God. That privilege cannot be taken away. I care not how savage and wicked the master may be, he cannot prevent you from praying in the midst of the night, and God hears and answers the prayer of all, slave or free.
But it seems to me that there is a new time coming for you colored people; a better day is dawning for you oppressed and down-trodden blacks. I don’t know that this is true, but I hope that the door is being opened for your deliverance. And now, how deeply you should ponder these words. If now you are unwilling to help yourselves nobody will be willing to help you. You must trust yourselves to the guidance of those who have had better opportunities and have acquired superior wisdom, if you would be carried through this crisis successfully. And I believe the good God will bless your efforts, and lift you up to a higher level than you have yet occupied, so that you and your children may become educated and industrious citizens. You must organize yourselves into families. Husbands must love their wives and children, clinging to them and turning from all others, and feeling that their highest object in life, next to serving the good God, is to do all they can for their families, working for them continually.
Good colored friends, you have a great work to do, and you are in a position of responsibility. The whole North, all the people in the Free States, are looking at you and the experiment now tried on your behalf with the deepest interest. This experiment is to give you freedom, position, home and your own families—wives, property, your own soil. You shall till and cultivate your own crops; you shall gather and sell the products of your industry for your own benefit; you shall own your own savings, and you shall be able to feel that God is prospering you from day to day and from year to year, and raising you to a higher level of goodness, religion and a nobler life.
Supposing you fail down here; that will be an end to the whole matter. It is like attaching a cable to a stranded vessel, and all the strength that can be mustered is put upon this rope to haul her off. If this only rope breaks the vessel is lost. God help you all and help us all to help you. If you are idle, vicious, indolent and negligent, you will fail and your last hope is gone; if you are not faithful you rivet eternally the fetters upon those who to-day are fastened down by fetters and suffer by the driver’s goad. You have in your hands the rescuing of those sufferers over whose sorrows you mourn continually. If you fail, what a dreadful responsibility it will be when you come to die to feel that the only great opportunity you had for serving yourselves and your oppressed race was allowed to slip.
And you, women, you must be careful of your children. You must teach them to be industrious, cleanly, obedient, and dutiful at all times. You must keep your houses neat and tidy, working all day, if necessary, to have them in the best possible condition, always thinking and contriving to make them cleaner and more comfortable. When your husband comes home from the labors and fatigues of the day, always have something good and nice for his supper, and speak kindly to him, for these little acts of love and attention will bring you happiness and joy.
And when you men go out to work, you must labor with diligence and zeal. It seems to me, had I the stimulus to work that you have that I could labor like a giant. Now you know who I am. My first duty here is to deal justly; second, to love mercy, and third, to walk humbly. First, justly—I shall endeavor to get you to do your duty faithfully. If you do I shall reward you; and if you refuse, then what comes next? Why, the wicked must be punished and made to do right. I will take the bad man by the throat and force him to his duty. I do not mean that I will take hold of him with my own hands, but with the strong arm of military power. Now do we understand each other? I am working for you already. I am told by your Superintendent that a gang of fifty men are building your houses at the rate of six a day. These houses are to make you more comfortable. You are to have a patch of ground, which you can call your own, to raise your own garden truck, and you may work for the Government for good wages. And you women must make your houses shine; you must plaster them and whitewash them, and gradually get furniture in your cabins, and a cooking-stove. I have arranged in such a way that you will get your clothing cheaper and better than before, and you are to have a school for your children. And you must have flowers in your gardens and blossoms before your doors. You will see in a little while how much happier you will be made. Are you not willing to work for this? Yes, God helping, you will all work. This is only for yourselves; but if you are successful, this plan will go all through the country, and we will have answered the question that has puzzled all good, thinking men in the world for one hundred years. They have asked, ‘What will you do with the black man after liberating him?’ We will show them what we will do. We will make him a useful, industrious citizen—give him the earnings of the sweat of his brow, and as a man, we will give him what the Lord ordained him to have.
I shall watch everything closely respecting this experiment. It is something to be permanent—more than for a day, more than for a year. Upon you depends whether this mighty result shall be worked out, and the day of jubilee come to God’s ransomed people.’”
Wharton also noted that:
“The white people have also had the advantage of religious instruction offered them during the past two Sabbaths, for the first time since the military occupation of South Carolina soil. An upper floor of one of the large commissary building has been appropriated as a place of worship, and the various regimental Chaplains are to officiate alternately. The first Sunday a discourse was delivered by the Rev. H.N. HUDSON, (Episcopal,) of the Volunteer Engineer Regiment, and day before yesterday the Rev. Dr. STRICKLAND, (Methodist,) Chaplain of the New-York Forty-eighth, favored us with a sermon. Gen. MITCHEL, who has instituted these religious privileges, is himself a regular attendant on the services.
Wharton then closed his letter with the following additional details:
“The propeller Trade Wind, Capt. Delanoy, was towed into this port last week by the gunboat Pocahontas, disabled by the bursting of her cylinder, when in latitude 25° north, longitude 79° 30′ west, on a voyage from New-York to New-Orleans, carrying a United States mail, and a cargo of Sutler’s goods. The damage is too great to be repaired here with our limited facilities, and she awaits a chance of being towed to New-York. Mr. RANKIN, of Philadelphia, chief engineer of the vessel, was severely sealed [sic] by the accident. The mails will be forwarded to New-Orleans by the first naval supply vessel going to that port.
The gunboat Quaker City at noon on Saturday last, ran [up] on the bar at North Edisto. Fears were [high] for the safely of the vessel, and the army steamers [?] Point and Rescue were sent to her aid. She was, however, out of danger when they reached her.
The work of organizing the troops in this Department into brigades has been commenced by Gen. MITCHEL, with a view to more system, and enhanced probability in future operations. Brig.-Gen. TERRY has been relieved of the command of the posts of the Florida Coast, and assigned to the Second Brigade, which is composed of the Seventh-sixth and Ninety-seventh Pennsylvania, the Seventh Connecticut, and the Third New-Hampshire Regiments….
By command of Maj.-Gen. O.M. MITCHEL,
W.P. [?], Maj.-Gen. and Chief of Staff ,
H. J. W.”
Sources:
- Beecher, Herbert W. History of the First Light Battery Connecticut Volunteers, 1861-1865, Vol. I. New York, New York: A. T. De La Mare Ptg. and Pub. Co., Ltd., 1901.
- “Florida’s Role in the Civil War: Supplier of the Confederacy.” Tampa, Florida: Florida Center for Instructional Technology, University of South Florida (College of Education), retrieved online, January 15, 2020.
- “IMPORTANT FROM PORT ROYAL.; The Expedition to Jacksonville, DESTRUCTION OF THE REBEL BATTERIES. CAPTURE OF A STEAMBOAT. Another Speech from Gen. Mitchell. His Policy and Sentiments on the Negro Question.” New York, New York: The New York Times, October 20, 1862.
- “Mitchelville: Freedom’s Home,” in “Think Like a Historian.” Beaufort County, South Carolina: Finding Freedom’s Home: Archaeology at Mitchelville, retrieved online, January 18, 2021.
- Proctor, Samuel. “Jacksonville During the Civil War,” in Florida Historical Quarterly, Vol. 41, No. 4, 1962, pp. 343-355. Orlando, Florida STARS (Showcase of Text, Archives, Research & Scholarship), University of Central, Florida.
- Reports of Lieut. Col. Tilghman H. Good, Forty-seventh Pennsylvania Infantry, in Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies, 1861-1865 (Microfilm M262). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Schmidt, Lewis G. A Civil War History of the 47th Regiment of Pennsylvania Veteran Volunteers. Allentown, Pennsylvania: Self-published, 1986.
- “Timucuan: The River War: The Timucuan Preserve in the Civil War.” Washington, DC: National Park Service and the U.S. Department of the Interior, retrieved online, January 18, 2021.




























You must be logged in to post a comment.