
Captain John Peter Shindel Gobin, Company C, 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers, shown here circa 1863, went on to become Lieutenant Governor of Pennsylvania after the war (public domain).
Still ruminating about the carnage that he and his fellow 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantrymen had survived just weeks earlier during the Battle of Pocotaligo, C Company Captain John Peter Shindel Gobin sat down in his quarters at his regiment’s encampment in Beaufort, South Carolina in mid-November 1862 and began to pen an update to a letter that he had recently written to friends back home. Despite his belief that he had “nothing to write home about,” his letter proved to be an important historical artifact — a handwritten, dated and signed eyewitness account that detailed what happened to multiple Union Army soldiers who had been wounded in action at that 1862 battle in South Carolina.
Head Quarters Co. C 47 P.V.
Beaufort S.C. Nov. 13. 1862
Dear Friends
I have just learned that a mail leaves for the North tomorrow morning although I have nothing particular to write about, and there is no telling when you will get it, as I understand vessels from here are now quarantined ten days at New York. Still I suppose you will be anxious to hear from me.
I have not heard from Sergt. Haupt today. Yesterday he was still living and improving, and I now have hopes of his recovery. I was down on Saturday last and both nurses and doctor promised me to do everything in their power to save him. If money or attention can save him it must be done.
The rest of the wounded of my Company are doing very well. All will recover, I think, and lose no limbs, but how many will be unfit for service I cannot yet tell. Billington, Kiehl, Barlton [sic, “Bartlow”], Sergt. Haupt and Leffler are yet at Hilton Head. Billington is on crutches and attending to Haupt or helping. Barlton [sic, “Bartlow”] and Leffler are also on crutches. Kiehl is walking about, but his jaw is badly shattered. Corp S. Y. Haupt is on duty. Haas’ wound is healing up nicely. Corp. Finck is about on crutches. O’Rourke, Holman, Lothard, Rine [sic, “Rhine”], and Larkins are in camp, getting along finely. Those who were wounded in the body, face and legs all get along much better than Sergt. Haupt who was wounded in the foot. His jaws were tightly locked the last time I saw him.
The Yellow fever is pretty bad at the Head, and I do not like to send any body down. I am holding a Court Martial, and keep very busy. The fever creates no alarm whatever here. No cases at all have occurred save those brought from Hilton Head. We have had two frosts and all feel satisfied that will settle the fever. Some good men have fallen victims to it. Gen. Mitchell [sic, Major-General Ormsby Mitchel] is much regretted here.
Sixty of my men are on picket under Lieut. Oyster, Lieut. Rees [sic, “Reese”] having been on the sick list. However he is well again. The balance of the men are all getting along finely. Warren McEwen had been sick but is well again. My health is excellent. Spirits ditto. I suppose however by the looks of things I will be kept in Court Martials for a month longer, the trial list being very large. The men begin to look on me as a kind of executioner as it seems I must be upon every Court held in the Dep’t [Department of the South].
We are waiting patiently and anxiously for a mail, not having had any news from the North since the 24th of last month. Three weeks without news seems a terrible time, when you come to realize it.
I wrote home from the Head the last time I was down. Was my last received. Write soon and give me all the news. With love to all
I remain
Yours JPSG
What Ultimately Happened to the Men Identified in That Gobin Letter?
The “Rees” and “Oyster” mentioned by Captain J. P. S. Gobin were his immediate subordinates, First Lieutenant William Reese and Second Lieutenant Daniel Oyster, who both ended up surviving the war. Reese would later be accused of cowardice during the 1864 Red River Campaign but cleared of that false charge, while Oyster would rise through the regiment’s ranks to become captain of Company C before being wounded in two different battles of Sheridan’s 1864 Shenandoah Valley Campaign.
The “Billington” and “Barlow” who had sustained leg wounds were Privates Samuel Billington and John Bartlow. Although both ultimately recovered from those wounds, Private Billington would later be deemed unable to continue serving with the 47th Pennsylvania and would be honorably discharged on a surgeon’s certificate of disability on July 1, 1863, while Private Bartlow would go on to become a sergeant with the 47th’s C Company, effective September 1, 1864, only to be killed in action just over a month later, during the Battle of Cedar Creek, Virginia.
“Corp. Finck” was Corporal William F. Finck, who had also been wounded in the leg and who also subsequently recovered and returned to duty. Unlike Sergeant Bartlow, however, he would survive a second wound that he would later sustain during the Battle of Cedar Creek and would be promoted to the rank of sergeant on April 1, 1865.
“Haas” was Private Jeremiah Haas, who had been wounded in the breast and face. Known as “Jerry” to his friends and family, he also eventually recovered and returned to duty, but was then mortally wounded in action during the Battle of Sabine Cross Roads near Mansfield, Louisiana on April 8, 1864 and died “almost instantly,” according to a letter written by his Company C comrade, Henry Wharton.
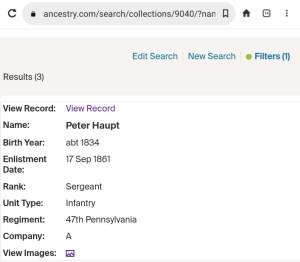
The “Haupts” were Sergeant Peter Haupt and his brother, Private Samuel Y. Haupt. Sergeant Peter Haupt, whose foot and ankle had been wounded at Pocotaligo, later developed lockjaw and died after contracting tetanus from the lead in the canister shot that had struck him. His brother, Samuel, however, survived. Wounded in the face and chin, Samuel would later be cleared for active duty and then be promoted steadily up through the ranks to become a first sergeant.
“Holman” was Private Conrad P. Holman, who had also been wounded in the face and who also recovered and returned to duty, would later be captured by Confederate troops during the Battle of Pleasant Hill in Louisiana on April 9, 1864 and be held as a prisoner of war (POW) at Camp Ford near Tyler, Texas until he was released during a prisoner exchange on July 22 of that same year.
“Kiehl” was Private Theodore Kiehl, whose jaw had shattered when his mouth was struck by a rifle ball at Pocotaligo, also recovered and returned to active duty. Sadly, he would later be killed in action on the grounds of Cooley’s farm near Winchester, Virginia during the Battle of Cedar Creek in October 1864.
“Larkins” and “Leffler” were Privates Michael F. Larkin and Charles W. Lefler, who had sustained wounds to the hip and side and/or arm and stomach (Larkins) and leg (Lefler) at Pocotaligo. They also both recovered and returned to active duty. Unlike so many of their comrades, however, they both survived their respective tenures of service and were both honorably discharged.
“Lothard” was actually Charles L. Marshall — one of several “mystery men” of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry. A native of Virginia who had relocated to Luzerne County, Pennsylvania to work in a coal mine prior to the American Civil War, he had enlisted as a private with the 47th Pennsylvania under the assumed name of “Thomas Lothard.” Shot in the head and/or body at Pocotaligo, he would ultimately recover and return to active duty, only to be wounded again in his head (top), body (right side) and left shin left during the Battle of Sabine Cross Roads in Louisiana on April 8, 1864. Later mistakenly labeled as a deserter, his military records were subsequently clarified to reflect his honorable discharge on January 7, 1866, as well as his legal name and alias.
“Warren McEwen” was Private Warren C. McEwen, whose illness would later become so persistent that he would be honorably discharged on a surgeon’s certificate of disability on December 7, 1862.
“O’Rourke” and “Rine” were Privates Richard O’Rourke and James R. Rhine, who had also sustained wounds to the side (O’Rourke) and leg (Rhine) at Pocotaligo, and would also recover, return to active duty, serve out their respective terms of enlistment, and be honorably discharged.
Veteran Volunteers
John Bartlow, William Finck, Samuel Haupt, Charles Marshall (as “Thomas Lothard”), Richard O’Rourke, and James Rhine were among multiple members of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry who would go on to be awarded the coveted title of “Veteran Volunteer” when they chose to re-enlist for additional tours of duty and helped to bring an end to one of the darkest times in America’s history.
Remember their names. Honor the sacrifices that they made.
Sources:
- Bates, Samuel P. History of Pennsylvania Volunteers, 1861-5, vol. 1. Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: B. Singerly, State Printer, 1869.
- Gobin, John Peter Shindel. Personal Letters, 1861-1865. Northumberland, Pennsylvania: Personal Collection of John Deppen.
- MacConkey, Alfred. “Tetanus: Its Prevention and Treatment by Means of Antitetanic Serum.” London, England: The British Medical Journal, vol. 2, no. 2806, October 10, 1914, pp. 609-614.
- Schmidt, Lewis G. A Civil War History of the 47th Regiment of Pennsylvania Veteran Volunteers. Allentown, Pennsylvania: Self-published, 1986.
- Wharton, Henry D. “Letters from the Sunbury Guards.” Sunbury, Pennsylvania: The Sunbury American, 1862.









You must be logged in to post a comment.