Roster: Company D, 47th Regiment, Pennsylvania Volunteers
History of Company D
1861-1862

Soldiers’ and Sailors’ Monument, New Bloomfield, Perry County, Pennsylvania, circa early 1900s (public domain).
The initial recruitment for members to fill Company D of the Pennsylvania Volunteers’ 47th Regiment was conducted in Bloomfield, Perry County, Pennsylvania. A number of this company’s earliest recruits had responded, following the fall of Fort Sumter in April 1861, to President Abraham Lincoln’s call for seventy-five thousand volunteers to help defend the nation’s capital. After completing their Three Months’ Service in July, a large contingent re-enrolled for three-year tours of duty.
Company D was led by Henry Durant Woodruff, a native of Waterbury, Connecticut who had been reared and educated in Windsor, New York until the age of eighteen when he relocated to Perry County, Pennsylvania. A citizen member of the local militia in Bloomfield and, professionally, a teacher and then innkeeper until 1861, Henry Woodruff had not only performed his own Three Month’s Service, but had actually raised the unit he commanded — Company D of the 2nd Pennsylvania Infantry, which was composed of residents from Bloomfield and other parts of Perry County. Commissioned as a captain with the 2nd Pennsylvania on 20 April 1861, he and his men served under General Robert Patterson at Winchester, Virginia. After honorably completing his Three Months’ Service, H. D. Woodruff mustered out at Camp Curtin, Harrisburg, Dauphin County on 26 July 1861.
Knowing the fight was not over, Henry D. Woodruff then promptly raised a second company. Recruiting men from Bloomfield again, he re-enrolled on 20 August 1861, and was again commissioned as a captain, mustering in at Camp Curtin on 31 August. His unit was then designated as Company D of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers, which had just been established weeks earlier by Tilghman H. Good.
Following a brief light infantry training period, Captain Woodruff and his company were sent by train with the 47th Pennsylvania to Washington, D.C. where they were stationed at “Camp Kalorama” on Kalorama Heights near Georgetown, about two miles from the White House, beginning 21 September. Henry D. Wharton, a musician with C Company, provided the following update on 22 September for readers of the Sunbury American, his hometown newspaper:
After a tedious ride we have, at last, safely arrived at the City of ‘magnificent distances.’ We left Harrisburg on Friday last at 1 o’clock A.M. and reached this camp yesterday (Saturday) at 4 P.M., as tired and worn out a sett [sic] of mortals as can possibly exist. On arriving at Washington we were marched to the ‘Soldiers Retreat,’ a building purposely erected for the benefit of the soldier, where every comfort is extended to him and the wants of the ‘inner man’ supplied.
After partaking of refreshments we were ordered into line and marched, about three miles, to this camp. So tired were the men, that on marching out, some gave out, and had to leave the ranks, but J. Boulton Young, our ‘little Zouave,’ stood it bravely, and acted like a veteran. So small a drummer is scarcely seen in the army, and on the march through Washington he was twice the recipient of three cheers.
We were reviewed by Gen. McClellan yesterday [21 September 1861] without our knowing it. All along the march we noticed a considerable number of officers, both mounted and on foot; the horse of one of the officers was so beautiful that he was noticed by the whole regiment, in fact, so wrapt [sic] up were they in the horse, the rider wasn’t noticed, and the boys were considerably mortified this morning on dis-covering they had missed the sight of, and the neglect of not saluting the soldier next in command to Gen. Scott.
Col. Good, who has command of our regiment, is an excellent man and a splendid soldier. He is a man of very few words, and is continually attending to his duties and the wants of the Regiment.
…. Our Regiment will now be put to hard work; such as drilling and the usual business of camp life, and the boys expect and hope an occasional ‘pop’ at the enemy.

Chain Bridge across the Potomac above Georgetown looking toward Virginia, 1861 (The Illustrated London News, public domain).
As a unit of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers, Company D became part of the federal service when the regiment officially mustered into the U.S. Army on 24 September. On 27 September, the 47th Pennsylvania was assigned to the 3rd Brigade of Brigadier-General Isaac Ingalls Stevens, which also included the 33rd, 49th and 79th New York regiments. By that afternoon, the 47th Pennsylvania was on the move again. Ordered onward by Brigadier-General Silas Casey, the Mississippi rifle-armed 47th Pennsylvania infantrymen marched behind their regimental band until reaching Camp Lyon, Maryland on the Potomac River’s eastern shore. At 5 p.m., they joined the 46th Pennsylvania in moving double-quick (one hundred and sixty-five steps per minute using thirty-three-inch steps) across the “Chain Bridge” marked on federal maps, and continued on for roughly another mile before being ordered to make camp.
The next morning, they broke camp and moved again. Marching toward Falls Church, Virginia, they arrived at Camp Advance around dusk. There, about two miles from the bridge they had crossed a day earlier, they re-pitched their tents in a deep ravine near a new federal fort under construction (Fort Ethan Allen). They had completed a roughly eight-mile trek, were situated fairly close to the headquarters of Brigadier-General William Farrar Smith (also known as “Baldy”), and were now part of the massive Army of the Potomac (“Mr. Lincoln’s Army”). Under Smith’s leadership, their regiment and brigade would help to defend the nation’s capital from the time of their September arrival through late January when the men of the 47th Pennsylvania would be shipped south.
Once again, Company C Musician Henry Wharton recapped the regiment’s activities, noting, via his 29 September letter home to the Sunbury American, that the 47th had changed camps three times in three days:
On Friday last we left Camp Kalorama, and the same night encamped about one mile from the Chain Bridge on the opposite side of the Potomac from Washington. The next morning, Saturday, we were ordered to this Camp [Camp Advance near Fort Ethan Allen, Virginia], one and a half miles from the one we occupied the night previous. I should have mentioned that we halted on a high hill (on our march here) at the Chain Bridge, called Camp Lyon, but were immediately ordered on this side of the river. On the route from Kalorama we were for two hours exposed to the hardest rain I ever experienced. Whew, it was a whopper; but the fellows stood it well – not a murmur – and they waited in their wet clothes until nine o’clock at night for their supper. Our Camp adjoins that of the N.Y. 79th (Highlanders.)….
We had not been in this Camp more than six hours before our boys were supplied with twenty rounds of ball and cartridge, and ordered to march and meet the enemy; they were out all night and got back to Camp at nine o’clock this morning, without having a fight. They are now in their tents taking a snooze preparatory to another march this morning…. I don’t know how long the boys will be gone, but the orders are to cook two days’ rations and take it with them in their haversacks….
There was a nice little affair came off at Lavensville [sic, Lewinsville], a few miles from here on Wednesday last; our troops surprised a party of rebels (much larger than our own.) killing ten, took a Major prisoner, and captured a large number of horses, sheep and cattle, besides a large quantity of corn and potatoes, and about ninety six tons of hay. A very nice day’s work. The boys are well, in fact, there is no sickness of any consequence at all in our Regiment….

The Big Chestnut Tree, Camp Griffin, Langley, Virginia, 1861 (U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Sometime during this phase of duty, as part of the 3rd Brigade, the 47th Pennsylvanians were moved to a site they initially christened “Camp Big Chestnut” in reference to a large chestnut tree located nearby. The site would eventually become known to the Keystone Staters as “Camp Griffin,” and was located roughly ten miles from Washington, D.C.
On 11 October, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers marched in the Grand Review at Bailey’s Cross Roads. In a letter sent to family and friends back home in mid-October, Captain John Peter Shindel Gobin (the leader of C Company who would be promoted in 1864 to lead the entire 47th Regiment) reported that companies D, A, C, F and I (the 47th Pennsylvania’s right wing) were ordered to picket duty after the left wing companies (B, G, K, E, and H) had been forced to return to camp by Confederate troops.
In his own letter of 13 October, Henry Wharton described their duties, as well as their new home:
The location of our camp is fine and the scenery would be splendid if the view was not obstructed by heavy thickets of pine and innumerable chesnut [sic] trees. The country around us is excellent for the Rebel scouts to display their bravery; that is, to lurk in the dense woods and pick off one of our unsuspecting pickets. Last night, however, they (the Rebels) calculated wide of their mark; some of the New York 33d boys were out on picket; some fourteen or fifteen shots were exchanged, when our side succeeded in bringing to the dust, (or rather mud,) an officer and two privates of the enemy’s mounted pickets. The officer was shot by a Lieutenant in Company H [?], of the 33d.
Our own boys have seen hard service since we have been on the ‘sacred soil.’ One day and night on picket, next day working on entrenchments at the Fort, (Ethan Allen.) another on guard, next on march and so on continually, but the hardest was on picket from last Thursday morning ‘till Saturday morning – all the time four miles from camp, and both of the nights the rain poured in torrents, so much so that their clothes were completely saturated with the rain. They stood it nobly – not one complaining; but from the size of their haversacks on their return, it is no wonder that they were satisfied and are so eager to go again tomorrow. I heard one of them say ‘there was such nice cabbage, sweet and Irish potatoes, turnips, &c., out where their duty called them, and then there was a likelihood of a Rebel sheep or young porker advancing over our lines and then he could take them as ‘contraband’ and have them for his own use.’ When they were out they saw about a dozen of the Rebel cavalry and would have had a bout with them, had it not been for…unlucky circumstance – one of the men caught the hammer of his rifle in the strap of his knapsack and caused his gun to fire; the Rebels heard the report and scampered in quick time….
The Unseen Foe
What may surprise readers most when studying the history of this and other Union regiments is that a fair number of “blue jackets” who lost their lives during the Civil War were claimed not by rifle or cannon fire, but by dysentery and other diseases commonly spread by troops suddenly placed in close military quarters, as well as by yellow fever and other tropical diseases which they encountered upon entering the Deep South.
Sergeant Frank M. Holt became one of the first of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers to die in this manner. He was laid to rest in the cemetery adjacent to the U.S. Soldiers’ and Airmen’s National Home in Washington, D.C. after succumbing to Variola (smallpox) at the Kalorama General Hospital in Washington, D.C. on 18 October 1861. He had only been a member of the 47th’s Company D since August, and was just twenty-three years old. His family also later created a cenotaph for him in his hometown cemetery in New Hampshire.
On Friday morning, 22 October 1861, the 47th engaged in a divisional review, described by historian Lewis Schmidt as massing “about 10,000 infantry, 1000 cavalry, and twenty pieces of artillery all in one big open field.” Less than a month later, in his letter of 17 November, Henry Wharton revealed more details about life at Camp Griffin:
This morning our brigade was out for inspection; arms, accoutrements [sic], clothing, knapsacks, etc, all were out through a thorough examination, and if I must say it myself, our company stood best, A No. 1, for cleanliness. We have a new commander to our Brigade, Brigadier General Brannen [sic], of the U.S. Army, and if looks are any criterion, I think he is a strict disciplinarian and one who will be as able to get his men out of danger as he is willing to lead them to battle….
The boys have plenty of work to do, such as piquet [sic] duty, standing guard, wood-chopping, police duty and day drill; but then they have the most substantial food; our rations consist of fresh beef (three times a week) pickled pork, pickled beef, smoked pork, fresh bread, daily, which is baked by our own bakers, the Quartermaster having procured portable ovens for that purpose, potatoes, split peas, beans, occasionally molasses and plenty of good coffee, so you see Uncle Sam supplies us plentifully….
A few nights ago our Company was out on piquet [sic]; it was a terrible night, raining very hard the whole night, and what made it worse, the boys had to stand well to their work and dare not leave to look for shelter. Some of them consider they are well paid for their exposure, as they captured two ancient muskets belonging to Secessia. One of them is of English manufacture, and the other has the Virginia militia mark on it. They are both in a dilapidated condition, but the boys hold them in high estimation as they are trophies from the enemy, and besides they were taken from the house of Mrs. Stewart, sister to the rebel Jackson who assassinated the lamented Ellsworth at Alexandria. The honorable lady, Mrs. Stewart, is now a prisoner at Washington and her house is the headquarters of the command of the piquets [sic]….
Since the success of the secret expedition, we have all kinds of rumors in camp. One is that our Brigade will be sent to the relief of Gen. Sherman, in South Carolina. The boys all desire it and the news in the ‘Press’ is correct, that a large force is to be sent there, I think their wish will be gratified….
On 21 November, the 47th participated in a morning divisional headquarters review monitored by Colonel Tilghman H. Good, followed by brigade and division drills all afternoon. According to Schmidt, “each man was supplied with ten blank cartridges.” Afterward, “Gen. Smith requested Gen. Brannan to inform Col. Good that the 47th was the best regiment in the whole division.”
As a reward — and in preparation for even bigger things to come, Brigadier-General John Milton Brannan obtained brand new Springfield rifles for every member of the 47th Pennsylvania.
1862
Next ordered to move from their Virginia encampment back to Maryland, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers left Camp Griffin at 8:30 a.m. on Wednesday, 22 January 1862, marching through deep mud with their equipment for three miles in order to reach the railroad station at Falls Church. Sent by rail to Alexandria, they then sailed the Potomac via the steamship City of Richmond to the Washington Arsenal, where they were reequipped before they were marched off for dinner and rest at the Soldiers’ Retreat in Washington, D.C. The next afternoon, the 47th Pennsylvanians hopped cars on the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad, and headed for Annapolis, Maryland. Arriving around 10 p.m., they were assigned quarters in barracks at the United States Naval Academy. They then spent that Friday through Monday (24-27 January 1862) loading their equipment and other supplies onto the steamship Oriental.
According to Schmidt and letters home from members of the regiment, those preparations ceased on Monday, 27 January, at 10 a.m. when:
The regiment was formed and instructed by Lt. Col. Alexander ‘that we were about drumming out a member who had behaved himself unlike a soldier.’ …. The prisoner, Pvt. James C. Robinson of Company I, was a 36 year old miner from Allentown who had been ‘disgracefully discharged’ by order of the War Department. Pvt. Robinson was marched out with martial music playing and a guard of nine men, two men on each side and five behind him at charge bayonets. The music then struck up with ‘Robinson Crusoe’ as the procession was marched up and down in front of the regiment, and Pvt. Robinson was marched out of the yard.
Reloading then resumed. By that afternoon, when the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers commenced boarding the Oriental, they were ferried to the big steamship by smaller steamers. The officers boarded last and, per the directive of Brigadier-General Brannan, the Oriental steamed away for the Deep South at 4 p.m. They were headed for Florida which, despite its secession from the Union, remained strategically important to the Union due to the presence of Forts Taylor and Jefferson in Key West and the Dry Tortugas.
Company D and their fellow 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers arrived in Key West in early February 1862. There, they were assigned to garrison Fort Taylor and drilled daily in heavy artillery tactics and other military strategies. During the weekend of Friday, 14 February, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers introduced their presence to Key West residents as the regiment paraded through the streets of the city. That Sunday, a number of the 47th Pennsylvanians mingled with local residents as they attended services at a local church.
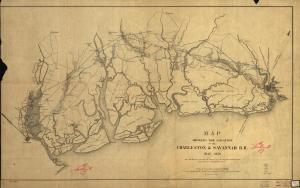
This 1856 map of the Charleston & Savannah Railroad shows the island of Hilton Head, South Carolina in relation to the towns of Beaufort and Pocotaligo (U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Next ordered to Hilton Head, South Carolina from mid-June through July, they camped near Fort Walker before relocating to the Beaufort District, Department of the South, roughly thirty-five miles away. Frequently assigned to hazardous picket detail north of their main camp, which put them at increased risk from enemy sniper fire, the members of the 47th Pennsylvania became known for their “attention to duty, discipline and soldierly bearing,” and “received the highest commendation from Generals Hunter and Brannan,” according to historian Samuel P. Bates.
Detachments from the regiment were also assigned to the Expedition to Fenwick Island (9 July) and the Demonstration against Pocotaligo (10 July).
On 12 July and 28 July 1862, respectively, Privates Washington Work and Robert Martin Harper, Captain Woodruff’s brother-in-law, were discharged on surgeons’ certificates and sent home to Perry County. Suffering from tuberculosis, Private Harper died at home in Landisburg on 16 August 1862, and was buried in his hometown cemetery. Private Work survived a month longer, passing away from complications related to dysentery at Petersburg in Perry County on 21 September 1862. He was buried at the Union Cemetery in Duncannon.
Meeting the Enemy Head On

Union Navy base of operations, Mayport Mills, circa 1862 (Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper, public domain).
Sent on a return expedition to Florida, Company D saw its first truly intense moments when it participated with the 47th Pennsylvania and other Union regiments in the capture of Saint John’s Bluff from 1 to 3 October. Led by Brigadier-General Brannan, a fifteen-hundred-plus Union force disembarked at Mayport Mills and Mount Pleasant Creek from troop carriers guarded by Union gunboats. Taking point, the 47th led the 3rd Brigade through twenty-five miles of dense, pine forested swamps populated with deadly snakes and alligators. By the time the expedition ended, the brigade had forced the Confederate Army to abandon its artillery battery atop Saint John’s Bluff, and had paved the way for the Union to occupy the town of Jacksonville, Florida.
From 5-15 October 1862, several young to middle-aged Black men who had escaped plantation enslavement in Beaufort, South Carolina enlisted with the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers. Initially assigned to kitchen duties, they would be officially mustered in for service with the regiment as Cooks and Under-Cooks at Morganza, Louisiana in June 1864. More men of color would continue to be added to the 47th Pennsylvania’s rosters in the weeks and years to come.

The challenging environment of the Charleston & Savannah Railroad was illustrated by Harper’s Weekly in 1865.
From 21-23 October, under the brigade and regimental commands of Colonel Tilghman H. Good and Lieutenant-Colonel George W. Alexander, the 47th engaged Confederate forces in and around Pocotaligo, South Carolina. Landing at Mackay’s Point, the men of the 47th were placed on point once again, but they and the 3rd Brigade were less fortunate this time.
Harried by snipers en route to the Pocotaligo Bridge, they met resistance from an entrenched, heavily fortified Confederate battery which opened fire on the Union troops as they entered an open cotton field. Those headed toward higher ground at the Frampton Plantation fared no better as they encountered artillery and infantry fire from the surrounding forests.
The Union soldiers grappled with the Confederates where they found them, pursuing the Rebels for four miles as they retreated to the bridge. There, the 47th relieved the 7th Connecticut. But the enemy was just too well armed. After two hours of intense fighting in an attempt to take the ravine and bridge, depleted ammunition forced the 47th to withdraw to Mackay’s Point.
Losses for the 47th were significant. Two officers and eighteen enlisted men died; two officers and another one hundred and fourteen enlisted men were wounded. Several resting places for men from the 47th still remain unidentified, the information lost to the sloppy records of Army Quartermaster and hospital personnel, or to the trauma-impaired memories of soldiers who hastily buried or were forced to leave behind the bodies of comrades upon receiving orders to retreat.
On 23 October, the 47th Pennsylvania returned to Hilton Head, where it served as the funeral honor guard for General Ormsby M. Mitchel, the commander of the U.S. Army’s 10th Corps and Department of the South who had succumbed to yellow fever on 30 October. The Mountains of Mitchel, a part of Mars’ South Pole discovered by Mitchel in 1846 while working as a University of Cincinnati astronomer, and Mitchelville, the first Freedmen’s town created after the Civil War, were both later named for him. Men from the 47th Pennsylvania were given the honor of firing the salute over his grave.
On 26 November, plagued by rheumatism from a prior bout of black scurvy, Private James Smith was discharged on a surgeon’s certificate of disability, and sent home.
1863

Fort Jefferson’s moat and wall, circa 1934, Dry Tortugas, Florida (C. E. Peterson, U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
By 1863, Captain Woodruff and the men of D Company were once again based with the 47th Pennsylvania in Florida. Having been ordered back to Key West on 15 November of 1862, much of 1863 was spent guarding federal installations in Florida as part of the 10th Corps, U.S. Department of the South. Companies A, B, C, E, G, and I garrisoned Fort Taylor in Key West while Companies D, F, H, and K garrisoned Fort Jefferson in Florida’s Dry Tortugas.
The members of Company D would remain at Fort Jefferson for just over five months. On 16 May, they were marched to the wharf at Fort Jefferson, where they climbed aboard yet another ship — this time to return to Fort Taylor, where they resumed garrison duties under the command of Colonel Tilghman H. Good.
On 16 July, they “presented a magnificent sword, sash, and belt” to Captain Woodruff “at the US Barracks in Key West,” according to Schmidt.
The company was formed in front of their quarters at 8 AM, across the barracks ground from Company C, and Pvt. George W. Baltozer, a 24 year old teacher from Perry County, made the following remarks on behalf of the company:
‘The motives that assemble us on the present occasion are based on our mature confidence, the martial skill, the intrepid heroism, and the undaunted intrepidity of our leader in arms. It is manifestive of our consciousness of your noble ability to wield in the defence [sic] of the rights of our country, this glittering weapon, that we place it in your protective hand. Receive it, sir, as a token of our estimation of your promotion of our ease and comfort in quietude, and for your chivalrous spirit on the sanguine field, when the heavens glared with fire, and the earth trembled ‘neath cannons’ roar. May it never rest in its scabbard ’till rebellion is crushed and traitorism is banished from the land, and peace spread her white wings from the St. John’s to the sunny banks of the Rio Grande. May it ever bespeak in the heart of him that wields it, bravery, loyalty, heroism, and philanthropy. That it may ever benefit you in the hour of peril, and that you may undauntingly use it as opportunity is afforded, is the very ardent wish of your most obedient servants.'”

Captain Henry Durant (“H.D.”) Woodruff, commanding officer of Company D, 2nd Pennsylvania Volunteers (April-July 1861) and Company D, 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers (31 August 1861 – 18 September 1864); public domain.
According to Schmidt, Captain Woodruff then responded to this touching tribute by presenting a surprisingly lengthy address to his men:
My companions in arms, your beautiful present is accepted with sincere satisfaction and heartfelt thanks. It affords the satisfaction that you still respect and have confidence in your commander, and he is thankful not only for the value of this noble gift, but for the rich token of your kind regard. And while I wear these arms and accoutrements, emblematical of my rank and office, may they never be worn unworthily, or the noble donors have cause to blush for the ungallant act of the wearer.
Two years have nearly elapsed since we have been associated as commander and commanded. Two years of privation and toil, yet your love for the cause and your ardor to serve your country has not abated.
When you entered upon this gigantic struggle, you were not prompted by large bribes or bounties, or intimidated by being forced in service by conscription. But inspired by a noble patriotism, you cheerfully volunteered for the longest period known to law.
Your conduct thus far has been in accordance with the honorable principles which caused you to volunteer. No discipline too strict, no privations too great, no toil too sore, but that your indomitable spirits have been able to accomplish, to undergo and overcome. And now allow me to say to you that I am proud of the noble men who compose this company; I am proud of your generous and gallant conduct; I am proud of your association; I am proud of the honor you have this day conferred upon your Captain.
In looking forward, I have no fears for you in the future, whatever you may be called on to do—in garrison—in the tented field, or on the sanguined plain, it will be bravely—it will be well done. Then until rebels and traitors shall become extinct, or have grounded their arms, and acknowledged the supremacy of the government and the law, let this our motto be: Give us death or give us liberty.
In his own account of that event, Sergeant Alan Wilson noted that Captain Woodruff’s speech was followed by three cheers by the men of D Company and a reception at which they ate and drank heartily in his honor.
The time spent here by the men of Company D and their fellow Union soldiers was notable also for the men’s commitment to preserving the Union. Many who could have returned home chose instead to re-enlist in order to finish the fight.
A letter to the New York Times, reprinted in the 30 April 1864 edition of the Semi-Weekly Wisconsin in Milwaukee, provided insight into the mindsets of the men from company D:
Remarkable History of a Military Company
To the Editor of the New York Times:Company D of the 47th Pennsylvania Regiment, a portion of which recently spent some time at the Soldiers’ Rest, in our city, on the way to Key West, can show the following record. There are in the company the following men:
William Powell, } Four brothers and a cousin.
John Powell,
Andrew Powell,
Solomon Powell,
Daniel Powell,John Brady, } All brothers.
William Brady,
Ackinson Brady,
Leonard Brady,Jacob Baltzer [sic], } Brothers.
George Baltzer [sic],
Benjamin Baltzer [sic],George Krosier [sic], } Brothers.
William Krosier [sic],
Jesse Krosier [sic],Edward Harper, } Brothers [sic] and Brothers-
Marvin Harper, in-law of the Captain.
George Harper,Jesse Shaffer, } Two Brothers and a Cousin.
Benjamin Shaffer,
William Shaffer,Wilson Tag, } Father and two sons; father
James Tag, served in Mexican War.
Richard Tag,John Clay, } Six pairs of brothers.
George Clay,
Jacob Charles,
Eli Charles,
John Reynolds,
Jesse Reynolds,
John Vance,
Jonathan Vance,
John Anthony,
Benjamin Anthony,
William Vertig [sic],
Franklin Vertig [sic],Isaac Baldwin, } Step-brothers.
Cyrus Taylor,These men all hail from Perry county, Pennsylvania. They are mainly of the old Holland stock, and lived within a circuit of fifteen miles. They are all re-enlisted men but two or three.
The company has been out over two years, most of the time at the extreme southern points. During eighteen months they lost but one man by sickness. They kept up strict salary regulations, commuted their rations of salt meat for fresh meat and vegetables, and saved by the operation from one hundred to one hundred thirty dollars a month, with which they made a company fund, appointing the Captain treasurer, and out of which whatever knick-nacks [sic] were needed could be purchased.
They always ate at a table, which they fixed with cross sticks, and had their food served from large bowls, each man having his place, as at home, which no one else was allowed to occupy. While the men were here, they showed that they were sober, cheerful, intelligent men, who had put their hearts into their work, and did not count any privations or sacrifices too great, if only the life of the country might thereby be maintained. During the whole term of their service, they had not had a man court-martialed.
They are commanded by Captain Henry D. Woodruff, a native of Binghamton, in this State, but long a resident of Pennsylvania. Their First Lieutenant is S. Ouchmuty [sic]; Second Lieutenant, George Stroop.
If any company can show a more striking record, it would be very interesting to know it.
The Harper brothers described above were actually brothers-in-law of Captain H. D. Woodruff.
1864
In early January 1864, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry was ordered to expand the Union’s reach even further by sending part of the regiment north to retake possession of Fort Myers, a federal installation that had been abandoned in 1858 following the U.S. government’s third war with the Seminole Indians. Per orders issued earlier in 1864 by Major-General D. P. Woodbury, Commanding Officer, U.S. Department of the Gulf, District of Key West and the Tortugas, that the fort be used to facilitate the Union’s Gulf Coast blockade, Captain Richard Graeffe and a group of men from Company A were charged with expanding the fort and conducting raids on area cattle herds to provide food for the growing Union troop presence across Florida. Graeffe and his men subsequently turned the fort into both their base of operations and a shelter for pro-Union supporters, escaped slaves, Confederate Army deserters, and others fleeing Rebel troops.
Meanwhile, all of the other companies of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry had already begun preparing for the regiment’s history-making journey to Louisiana. As part of those preparations, D Company Sergeant Jesse Meadath was promoted to the rank of first sergeant on 30 January.
Boarding yet another steamer — the Charles Thomas — on 25 February 1864, the men from Companies B, C, D, I, and K of the 47th Pennsylvania headed for Algiers, Louisiana (across the river from New Orleans), followed on 1 March by other members of the regiment from Companies E, F, G, and H who had been stationed at Fort Jefferson in the Dry Tortugas. Upon the second group’s arrival, the now almost fully reconstituted regiment moved by train on 28 February to Brashear City before heading to Franklin by steamer through the Bayou Teche. There, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry joined the 2nd Brigade, 1st Division of the Department of the Gulf’s 19th Army Corps, and became the only Pennsylvania regiment to serve in the Red River Campaign of Union Major-General Nathaniel P. Banks.
Red River Campaign
From 14-26 March, the 47th passed through New Iberia, Vermilionville, Opelousas, and Washington while en route to Alexandria and Natchitoches, Louisiana. Sadly, Private William Mays of Company D would be among those from the 47th who would not survive the Red River experience. One of the early casualties in this campaign, he died from disease-related complications at the Union’s General Hospital in New Orleans on 30 March 1864.
From 4-5 April 1864, the 47th Pennsylvania added to its roster of young Black soldiers when eighteen-year-old John Bullard enrolled for service with Company D at Natchitoches, and Aaron and James Bullard, Samuel Jones, and Hamilton Blanchard (also known as John Hamilton) enrolled with other companies of the 47th. According to his entry in the Civil War Veterans’ Card File at the Pennsylvania State Archives, John Bullard was officially mustered in for duty on 22 June “as (Colored) Cook.”
Often short on food and water, the regiment encamped briefly at Pleasant Hill the night of 7 April before continuing on the next day, marching until mid-afternoon.
Rushed into battle ahead of other regiments in the 2nd Division, sixty members of the 47th were cut down on 8 April during the volley of fire unleashed during the Battle of Sabine Cross Roads. The fighting waned only when darkness fell. Exhausted, those who were uninjured collapsed beside the gravely wounded. After midnight, the surviving Union troops withdrew to Pleasant Hill.
The next day, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were ordered into a critically important defensive position at the far right of the Union lines, their right flank spreading up onto a high bluff. By 3 p.m., after enduring a midday charge by the troops of Confederate Major-General Richard Taylor (a plantation owner and son of Zachary Taylor, former president of the United States), the brutal fighting still showed no signs of ending. Suddenly, just as the 47th was shifting to the left side of the massed Union forces, the men of the 47th Pennsylvania were forced to bolster the 165th New York’s buckling lines by blocking another Confederate assault, during what has since become known as the Battle of Pleasant Hill.
Casualties were once again severe. Lieutenant-Colonel Alexander was nearly killed, and the regiment’s two color-bearers, both from Company C, were also wounded while preventing the American flag from falling into enemy hands. Private Ephraim Clouser of Company D was shot in his right knee and subsequently captured by Confederate troops, and Corporal Isaac Baldwin was also wounded, but avoided a similar fate.
This, too, was a history making moment, as the 47th became the only Pennsylvania regiment to have men held at Camp Ford, the largest Confederate prison camp operating west of the Mississippi River. Confined as POWs in deteriorating conditions while often subject to harsh treatment by Confederate officers and guards, most of the 47th Pennsylvanians survived to be released during prisoner exchanges in July, August or November 1864. Sergeant James Crownover, Private James Downs, Corporal John Garber Miller and Private William J. Smith were four of the fortunate who survived. Downs, Miller and Smith were released on 22 July. Crownover, who had been wounded in battle before being taken captive, was commissioned, but not mustered as a second lieutenant on 31 August 1864 (while in captivity with the hope that he would be afforded better treatment), and was finally released on 25 November 1864.
Following what some historians have called a rout by Confederates at Pleasant Hill and others have labeled a technical victory for the Union or a draw for both sides, the 47th Pennsylvanians fell back to Grand Ecore, where they remained for a total of eleven days. After engaging in the hard labor of strengthening regimental and brigade fortifications in a brutal climate, they moved back to Natchitoches Parish on 22 April 1864, arriving in Cloutierville at 10 p.m. that night after marching forty-five miles. En route, the Union forces were attacked again — this time in the rear, but they were able to quickly end the encounter and continue on.
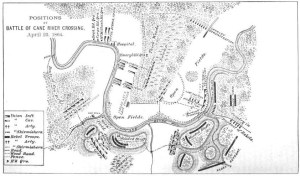
The 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were stationed just to the left of the “Thick Woods” with Emory’s 2nd Brigade, 1st Division as shown on this map of Union troop positions for the Battle of Cane River Crossing at Monett’s Ferry, Louisiana, 23 April 1864 (Major-General Nathaniel Banks’ official Red River Campaign Report, public domain).
On 23 April, episodic skirmishing quickly roared into the flames of a robust fight as 47th Pennsylvanians and other members of their brigade engaged the Confederate troops of Brigadier-General Hamilton Bee in the Battle of Cane River (also known as “the Affair at Monett’s Ferry.” Part of the advance party led by Brigadier-General William Emory, the 47th Pennsylvania supported Emory’s artillery as it countered the barrage from the Confederate artillery’s twenty-pound Parrott guns and raking fire from enemy troops situated near a bayou and on a bluff.
Meanwhile, other troops under Emory’s command worked their way across the Cane River, attacked Bee’s flank, and forced a Rebel retreat. Those Union troops then erected a series of pontoon bridges, enabling the 47th and other remaining Union soldiers to make the Cane River Crossing the next day. As the Confederates retreated, they torched their own food stores, as well as the cotton supplies of their fellow southerners.
In a letter penned from Morganza, Louisiana on 29 May, Henry Wharton described what had happened to the 47th Pennsylvanians during and immediately after making camp at Grand Ecore:
Our sojourn at Grand Ecore was for eleven days, during which time our position was well fortified by entrenchments for a length of five miles, made of heavy logs, five feet high and six feet wide, filled in with dirt. In front of this, trees were felled for a distance of two hundred yards, so that if the enemy attacked we had an open space before us which would enable our forces to repel them and follow if necessary. But our labor seemed to the men as useless, for on the morning of 22d April, the army abandoned these works and started for Alexandria. From our scouts it was ascertained that the enemy had passed some miles to our left with the intention of making a stand against our right at Bayou Cane, where there is a high bluff and dense woods, and at the same attack Smith’s forces who were bringing up the rear. This first day was a hard one on the boys, for by ten o’clock at night they made Cloutierville, a distance of forty-five miles. On that day the rear was attacked which caused our forces to reverse their front and form in line of battle, expecting too, to go back to the relief of Smith, but he needed no assistance, sending word to the front that he had ‘whipped them, and could do it again.’ It was well that Banks made so long a march on that day, for on the next we found the enemy prepared to carry out their design of attacking us front and rear. Skirmishing commenced early in the morning and as our columns advanced he fell back towards the bayou, when we soon discovered the position of their batteries on the bluff. There was then an artillery duel by the smaller pieces, and some sharp fighting by the cavalry, when the ‘mule battery,’ twenty pound Parrott guns, opened a heavy fire, which soon dislodged them, forcing the chivalry to flee in a manner not at all suitable to their boasted courage. Before this one cavalry, the 3d Brigade of the 1st Div., and Birges’ brigade of the second, had crossed the bayou and were doing good service, which, with the other work, made the enemy show their heels. The 3d brigade done some daring deeds in this fight, as also did the cavalry. In one instance the 3d charged up a hill almost perpendicular, driving the enemy back by the bayonet without firing a gun. The woods on this bluff was so thick that the cavalry had to dismount and fight on foot. During the whole of the day, our brigade, the 2d was supporting artillery, under fire all the time, and could not give Mr. Reb a return shot.
While we were fighting in front, Smith was engaged some miles in the rear, but he done his part well and drove them back. The rebel commanders thought by attacking us in the rear, and having a large face on the bluffs, they would be able to capture our train and take us all prisoners, but in this they were mistaken, for our march was so rapid that we were on them before they had thrown up the necessary earthworks. Besides they underrated the amount of our artillery, calculating from the number engaged at Pleasant Hill. The rebel prisoners say it ‘seems as though the Yankees manufacture, on short notice, artillery to order, and the men are furnished with wings when they wish to make a certain point.
The damage done to the Confederate cause by the burning of cotton was immense. On the night of the 22d our route was lighted up for miles and millions of dollars worth of this production was destroyed. This loss will be felt more by Davis & Co., than several defeats in this region, for the basis of the loan in England was on the cotton of Western Louisiana.
After the rebels had fled from the bluff the negro troops put down the pontoons, and by ten that night we were six miles beyond the bayou safely encamped. The next morning we moved forward and in two days were in Alexandria. Johnnys followed Smith’s forces, keeping out of range of his guns, except when he had gained the eminence across the bayou, when he punished them (the rebs) severely.

Christened “Bailey’s Dam” in reference to the Union officer who ordered its construction, Lieutenant-Colonel Joseph Bailey, this timber dam built by the Union Army on the Red River near Alexandria, Louisiana in May 1864 facilitated Union gunboat passage (public domain).
Having finally reached Alexandria on 26 April, they learned they would remain at their latest new camp for at least two weeks. Placed temporarily under the command of Lieutenant-Colonel Joseph Bailey, they were assigned yet again to the hard labor of fortification work, helping to erect “Bailey’s Dam,” a timber structure that enabled Union gunboats to more easily make their way back down the Red River. According to Wharton:
We were at Alexandria seventeen days, during which time the men were kept busy at throwing up earthworks, foraging and three times went out some distance to meet the enemy, but they did not make their appearance in numbers large enough for an engagement. The water in the Red river had fallen so much that it prevented the gunboats from operating with us, and kept our transports from supplying the troops with rations, (and you know soldiers, like other people, will eat) so Banks was compelled to relinquish his designs on Shreveport and fall back to the Mississippi. To do this a large dam had to be built on the falls at Alexandria to get the ironclads down the river. After a great deal labor this was accomplished and by the morning of May 13th the last one was through the shute [sic], when we bade adieu to Alexandria, marching through the town with banners flying and keeping step to the music of ‘Rally around the flag,’ and ‘When this cruel war is over.’ The next morning, at our camping place, the fleet of boats passed us, when we were informed that Alexandria had been destroyed by fire – the act of a dissatisfied citizen and several negroes. Incendiary acts were strictly forbidden in a general order the day before we left the place, and a cavalry guard was left in the rear to see the order enforced. After marching a few miles skirmishing commenced in front between the cavalry and the enemy in riflepits [sic] on the bank of the river, but they were easily driven away. When we came up we discovered their pits and places where there had been batteries planted. At this point the John Warren, an unarmed transport, on which were sick soldiers and women, was fired into and sunk, killing many and those that were not drowned taken prisoners. A tin-clad gunboat was destroyed at the same place, by which we lost a large mail. Many letters and directed envelopes were found on the bank – thrown there after the contents had been read by the unprincipled scoundrels. The inhumanity of Guerrilla bands in this department is beyond belief, and if one did not know the truth of it or saw some of their barbarities, he would write it down as the story of a ‘reliable gentleman’ or as told by an ‘intelligent contraband.’ Not satisfied with his murderous intent on unarmed transports he fires into the Hospital steamer Laurel Hill, with four hundred sick on board. This boat had the usual hospital signal floating fore and aft, yet, notwithstanding all this, and the customs of war, they fired on them, proving by this act that they are more hardened than the Indians on the frontier.
On Sunday, May 15, we left the river road and took a short route through the woods, saving considerable distance. The windings of Red river are so numerous that it resembles the tape-worm railroad wherewith the politicians frightened the dear people during the administration of Ritner and Stevens. – We stopped several hours in the woods to leave cavalry pass, when we moved forward and by four o’clock emerged into a large open plain where we formed in line of battle, expecting a regular engagement. The enemy, however, retired and we advanced ‘till dark, when the forces halted for the night, with orders to rest on their arms. – ‘Twas here that Banks rode through our regiment, amidst the cheers of the boys, and gave the pleasant news that Grant had defeated Lee.

“Sleeping on Their Arms” by Winslow Homer (Harper’s Weekly, 21 May 1864).
Having entered Avoyelles Parish, they “rested on their arms” for the night, half-dozing without pitching their tents, but with their rifles right beside them. They were now positioned just outside of Marksville, Louisiana on the eve of the 16 May 1864 Battle of Mansura, which unfolded as follows, according to Wharton:
Early next morning we marched through Marksville into a prairie nine miles long and six wide where every preparation was made for a fight. The whole of our force was formed in line, in support of artillery in front, who commenced operations on the enemy driving him gradually from the prairie into the woods. As the enemy retreated before the heavy fire of our artillery, the infantry advanced in line until they reached Mousoula [sic], where they formed in column, taking the whole field in an attempt to flank the enemy, but their running qualities were so good that we were foiled. The maneuvring [sic] of the troops was handsomely done, and the movements was [sic] one of the finest things of the war. The fight of artillery was a steady one of five miles. The enemy merely stood that they might cover the retreat of their infantry and train under cover of their artillery. Our loss was slight. Of the rebels we could not ascertain correctly, but learned from citizens who had secreted themselves during the fight, that they had many killed and wounded, who threw them into wagons, promiscuously, and drove them off so that we could not learn their casualties. The next day we moved to Simmsport on the Achafalaya [sic] river, where a bridge was made by putting the transports side by side, which enabled the troops and train to pass safely over. – The day before we crossed the rebels attacked Smith, thinking it was but the rear guard, in which they, the graybacks, were awfully cut up, and four hundred prisoners fell into our hands. Our loss in killed and wounded was ninety. This fight was the last one of the expedition. The whole of the force is safe on the Mississippi, gunboats, transports and trains. The 16th and 17th have gone to their old commands.
It is amusing to read the statements of correspondents to papers North, concerning our movements and the losses of our army. I have it from the best source that the Federal loss from Franklin to Mansfield, and from their [sic] to this point does not exceed thirty-five hundred in killed, wounded and missing, while that of the rebels is over eight thousand.

Union Army base at Morganza Bend, Louisiana, circa 1863-1865 (U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Continuing on, the surviving members of the 47th marched for Simmesport and then Morganza, where they made camp again. According to Wharton, the members of Company C were sent on a special mission which took them on an intense one hundred and twenty-mile journey:
Company C, on last Saturday was detailed by the General in command of the Division to take one hundred and eighty-seven prisoners (rebs) to New Orleans. This they done [sic] satisfactorily and returned yesterday to their regiment, ready for duty. While in the City some of the boys made Captain Gobin quite a handsome present, to show their appreciation of him as an officer gentleman.
Wharton also provided the following update regarding Company C, which had rejoined the bulk of the 47th Pennsylvania on 28 May 1864:
The boys are well. James Kennedy who was wounded at Pleasant Hill, died at New Orleans hospital a few days ago. His friends in the company were pleased to learn that Dr. Dodge of Sunbury, now of the U.S. Steamer Octorora, was with him in his last moments, and ministered to his wants. The Doctor was one of the Surgeons from the Navy who volunteered when our wounded was sent to New Orleans.
While encamped at Morganza, the nine formerly enslaved Black men who had enlisted with the 47th Pennsylvania in Beaufort, South Carolina (1862) and Natchitoches, Louisiana (April 1864) were officially mustered into the regiment between 20-24 June 1864. The regiment then moved on once again, and arrived in New Orleans in late June.
As they did during their tour through the Carolinas and Florida, the men of the 47th had battled the elements and disease, as well as the Confederate Army, in order to survive and continue to defend their nation. But the Red River Campaign’s most senior leader, Union Major-General Nathaniel P. Banks, would not. Removed from command amid the controversy regarding the Union Army’s successes and failures, he was placed on leave by President Abraham Lincoln. He later redeemed himself by spending much of his time in Washington, D.C. as a Reconstruction advocate for the people of Louisiana.
Sheridan’s 1864 Shenandoah Valley Campaign
Still able and willing to fight after their time in Bayou country, the soldiers of Company D and their fellow members of the 47th Pennsylvania’s Companies A, C, D, E, F, H, and I boarded the U.S. McClellan and steamed away for the East Coast beginning 7 July 1864.
Following their arrival in Virginia and a memorable encounter with President Abraham Lincoln, they then joined up with Major-General David Hunter’s forces at Snicker’s Gap in mid-July 1864. There, they engaged in the Battle of Cool Spring and, once again, assisted in defending Washington, D.C. while also helping to drive Rebel troops from Maryland.
Attached to the Middle Military Division, U.S. Army of the Shenandoah beginning in August, the opening days of September saw the departure of several 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers who had served honorably, including Company D’s Captain Henry Woodruff, First Lieutenant Samuel Auchmuty, Sergeants Henry Heikel and Alex Wilson, and Corporals Cornelius Stewart and Samuel A. M. Reed. All mustered out on 18 September 1864 upon expiration of their service terms. At least one of those departures — that of Sergeant Henry Heikel — might have been prevented had senior military leaders been more responsive to regimental advancement requests. According to historian Lewis Schmidt:
On Tuesday [9 August 1864], the 47th prepared to resume its march, this time from Halltown back to Middletown where the regiment arrived on Friday. Letters from both Col. Good and Capt. Gobin to the Governor and the Adjutant General of Pa. were written regarding promotions on this date from ‘In the field near Halltown’. In Company D, 54 of the non-commissioned officers and Privates signed a letter to the Governor’s office requesting that Sgt. Henry Heikel be promoted to Captain and Cpl. George W. Clay to Lieutenant. They were unsuccessful and this time, and other more senior men would be promoted to these positions. Sgt. Heikel would muster out the following month at the expiration of his term, and Cpl. Clay would eventually attained the rank of 1st Lieutenant on June 2, 1865.
And experienced, battle-tested leaders would be needed in the days and weeks ahead because those members of the 47th who did opt to remain on duty were about to engage in their regiment’s greatest moments of valor. The first significant test of this duty phase came during the first week of September as the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers fought in the Battle of Berryville from 3-4 September, and then engaged in related post-battle skirmishes with the enemy over subsequent days.
Battles of Opequan and Fisher’s Hill — September 1864
Together with other regiments under the command of Union Major-General Philip H. (“Little Phil”) Sheridan and Brigadier-General William H. Emory, commander of the 19th Corps, the members of Company D and their fellow 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers helped to inflict heavy casualties on Lieutenant-General Jubal Early’s Confederate forces during the Battle of Opequan (also spelled as “Opequon” and referred to as “Third Winchester”). The battle is still considered by many historians to be one of the most important during Sheridan’s 1864 campaign; the Union’s victory here helped to ensure the reelection of President Abraham Lincoln.
The 47th Pennsylvania’s march toward destiny at Opequan began at 2 a.m. on 19 September 1864 as the regiment left camp and joined up with others in the Union’s 19th Corps. After advancing slowly from Berryville toward Winchester, the 19th Corps became bogged down for several hours by the massive movement of Union troops and supply wagons, enabling Early’s men to dig in. After finally reaching the Opequan Creek, Sheridan’s men came face to face with the Confederate Army commanded by Early. The fighting, which began in earnest at noon, was long and brutal. The Union’s left flank (6th Corps) took a beating from Confederate artillery stationed on high ground.

Victory of Philip Sheridan’s Union Army over Jubal Early’s Confederate forces, Battle of Opequan, 19 September 1864 (Kurz & Allison, circa 1893, U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Meanwhile, the 47th Pennsylvania and the 19th Corps were directed by Brigadier-General William Emory to attack and pursue Major-General John B. Gordon’s Confederate forces. Some success was achieved, but casualties mounted as another Confederate artillery group opened fire on Union troops trying to cross a clearing. When a nearly fatal gap began to open between the 6th and 19th Corps, Sheridan sent in units led by Brigadier-Generals Emory Upton and David A. Russell. Russell, hit twice — once in the chest, was mortally wounded. The 47th Pennsylvania opened its lines long enough to enable the Union cavalry under William Woods Averell and the foot soldiers of General George Crook to charge the Confederates’ left flank.
The 19th Corps, with the 47th in the thick of the fighting, then began pushing the Confederates back. Early’s “grays” retreated in the face of the valor displayed by Sheridan’s “blue jackets.” Leaving twenty,-five hundred wounded behind, the Rebels retreated to Fisher’s Hill (21-22 September), eight miles south of Winchester, and then to Waynesboro, following a successful early morning flanking attack by Sheridan’s Union men which outnumbered Early’s three to one.
Afterward, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were sent out on skirmishing parties before making camp at Cedar Creek. The day of the Opequan encounter (19 September 1864), Corporals John V. Brady and John G. Miller of Company were both promoted to the rank of sergeant, and Privates Jacob P. Baltozer, William D. Hays, Noble Henkle, William Powell, John E. L. Roth, and Benjamin F. Shaffer all received promotions to the rank of corporal.
On 22 September 1864, First Sergeant George W. Kosier became a first lieutenant.
Moving forward, they and other members of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers would continue to distinguish themselves in battle, but they would do so without two more of their respected commanders: Colonel Tilghman Good and Good’s second in command, Lieutenant-Colonel George Alexander, who mustered out 23-24 September upon expiration of their respective terms of service.
Fortunately, they were replaced by others equally admired both for temperament and their front line experience: Second Lieutenant George Stroop, who was promoted to lead Company D, and at the regimental level, John Peter Shindel Gobin, Charles W. Abbott and Levi Stuber.
Battle of Cedar Creek, 19 October 1864

Alfred Waud’s 1864 sketch, “Surprise at Cedar Creek,” captured the flanking attack on the rear of Union Brigadier-General William Emory’s 19th Corps by Lieutenant-General Jubal Early’s Confederate army, and the subsequent resistance by Emory’s troops from their Union rifle-pit positions, 19 October 1864 (public domain).
It was during the fall of 1864 that General Philip Sheridan began the first of the Union’s true “scorched earth” campaigns, starving the enemy into submission by destroying Virginia’s crops and farming infrastructure. Viewed through today’s lens of history as inhumane, the strategy claimed many innocents — civilians whose lives were cut short by their inability to find food. This same strategy, however, almost certainly contributed to the further turning of the war’s tide in the Union’s favor during the Battle of Cedar Creek on 19 October 1864. Successful throughout most of their engagement with Union forces at Cedar Creek, Early’s Confederate troops began peeling off in ever growing numbers to forage for food, thus enabling the 47th Pennsylvania and others under Sheridan’s command to rally.
From a military standpoint, it was another impressive, but heartrending day. During the morning of 19 October, Early launched a surprise attack directly on Sheridan’s Cedar Creek-encamped forces. Early’s men were able to capture Union weapons while freeing a number of Confederates who had been taken prisoner during previous battles — all while pushing seven Union divisions back. According to Bates:
When the Army of West Virginia, under Crook, was surprised and driven from its works, the Second Brigade, with the Forty-seventh on the right, was thrown into the breach to arrest the retreat…. Scarcely was it in position before the enemy came suddenly upon it, under the cover of fog. The right of the regiment was thrown back until it was almost a semi-circle. The brigade, only fifteen hundred strong, was contending against Gordon’s entire division, and was forced to retire, but, in comparative good order, exposed, as it was, to raking fire. Repeatedly forming, as it was pushed back, and making a stand at every available point, it finally succeeded in checking the enemy’s onset, when General Sheridan suddenly appeared upon the field, who ‘met his crest-fallen, shattered battalions, without a word of reproach, but joyously swinging his cap, shouted to the stragglers, as he rode rapidly past them – “Face the other way, boys! We are going back to our camp! We are going to lick them out of their boots!'”

Sheridan Rallying His Troops, Battle of Cedar Creek, Virginia, 19 October 1864 (U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
The Union’s counterattack punched Early’s forces into submission, and the men of the 47th were commended for their heroism by General Stephen Thomas who, in 1892, was awarded the Medal of Honor for his own “distinguished conduct in a desperate hand-to-hand encounter, in which the advance of the enemy was checked” that day. Bates described the 47th’s actions:
When the final grand charge was made, the regiment moved at nearly right angles with the rebel front. The brigade charged gallantly, and the entire line, making a left wheel, came down on his flank, while engaging the Sixth Corps, when he went “whirling up the valley” in confusion. In the pursuit to Fisher’s Hill, the regiment led, and upon its arrival was placed on the skirmish line, where it remained until twelve o’clock noon of the following day. The army was attacked at early dawn…no respite was given to take food until the pursuit was ended.
Once again, the casualties for the 47th were high. Perry County resident and Regimental Chaplain William Rodrock suffered a near miss as a bullet pierced his cap, but Sergeant William Pyers, the C Company man who had so gallantly rescued the flag at Pleasant Hill was cut down and later buried on the battlefield. Corporal Edward Harper of Company D was wounded, but survived, as did Corporal Isaac Baldwin, who had been wounded earlier at Pleasant Hill.
Still others, who had been captured and transported from the Cedar Creek battlefield area to the Confederate Army’s notorious Salisbury, North Carolina prison camp, died there from disease or starvation within a few short weeks after their confinement.
On 23 October 1864, Regimental Orders, No. 70 was issued, directing that John Bullard be transferred from the 47th Pennsylvania’s Company D to I Company. Bullard, one of nine formerly enslaved Black men who had mustered into the 47th Pennsylvania as cooks or under cooks while the regiment was stationed in South Carolina and Louisiana, would continue to serve with I Company for the duration of the war and muster out with his regiment on Christmas Day in December 1865.
Following these major engagements, the 47th was ordered to Camp Russell near Winchester from November through most of December. On 14 November, Second Lieutenant George Stroop was promoted to the rank of captain. Rested and somewhat healed, the 47th was then ordered to outpost and railroad guard duties at Camp Fairview in Charlestown, West Virginia five days before Christmas.
1865 — 1866
On 20 January 1865, Corporal Isaac Baldwin, twice wounded in battle, was promoted to the rank of sergeant; on 30 January, Corporal George W. Clay became a second lieutenant; on 30 March, Captain George Stroop was also promoted again, this time to the rank of major.
Assigned first to the Provisional Division of the 2nd Brigade of the U.S. Army of the Shenandoah in February, the men of the 47th moved, via Winchester and Kernstown, back to Washington, D.C. where, on 19 April, they were again responsible for helping to defend the nation’s capital — this time following the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln. Stationed at Camp Brightwood, they received new uniforms and were resupplied with ammunition.

Spectators gather for the Grand Review of the Armies, 23-24 May 1865, beside the crepe-draped U.S. Capitol, flag at half-staff following the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln (Matthew Brady, U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Letters sent by 47th Pennsylvanians to family and friend during this time, and post-war interviews by newspaper reporters of 47th Pennsylvania veterans, confirm that at least one 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer was given the high honor of guarding President Lincoln’s funeral train while others may have guarded the key Lincoln assassination conspirators during the early days of their imprisonment and trial, which began on 9 May, 1865. During this phase of duty, the regiment was headquartered at Camp Brightwood in the Brightwood section of Washington, D.C.
Attached to Dwight’s Division of the 2nd Brigade of the U.S. Department of Washington’s 22nd Corps, the 47th Pennsylvania also participated in the Union’s Grand Review of the National Armies on 23 May.
Captain Levi Stuber of Company I was promoted to the rank of major with the regiment’s central staff during this time. On 1-2 June 1865, First Lieutenant George W. Kosier was promoted to the rank of captain and leadership of Company D prior to the mustering out of Major George Stroop, who had completed his term of service; Second Lieutenant George W. Clay was promoted to the rank of first lieutenant.
Reconstruction

Ruins of Charleston, South Carolina as seen from the Circular Church, 1865 (U.S. National Archives and Records Administration, public domain).
On their final southern tour, Company D and their fellow 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers served in Savannah, Georgia in early June. Attached again to Dwight’s Division, this time they were members of the 3rd Brigade, U.S. Department of the South. Relieving the 165th New York Volunteers in July, they were quartered in the former mansion of the Confederate Secretary of the Treasury. But once again, disease stalked the 47th. Many who did not survive were initially interred in Charleston’s Magnolia Cemetery.
The day after Independence Day, Corporal Theodore Troup was promoted to the rank of sergeant, Sergeant James Crownover was advanced to the rank of first sergeant and First Sergeant Jesse Meadath became a second lieutenant.
Then, beginning on Christmas day of that year, the majority of the men of Company D, 47th Regiment, Pennsylvania Volunteers finally began to honorably muster out at Charleston, South Carolina. Following a stormy voyage home, the weary men disembarked in New York City, and were then transported by train to Philadelphia, where, at Camp Cadwalader on 9 January 1866, the 47th Pennsylvania Veteran Volunteers were officially given their discharge papers.
Many went on to live long full lives. Some, like their former commanding officers, Tilghman H. Good, contributed greatly to their communities. Far more faded quietly into the background, content to take up farming, carpentry or other trades to support their new and growing families.
Sources:
- “Assassination of President Abraham Lincoln.” Washington, D.C.: U.S. Library of Congress, retrieved online May 21, 2025.
- Bates, Samuel P. History of Pennsylvania Volunteers, 1861-5, vol. 1. Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: B. Singerly, State Printer, 1869.
- “Battleground National Cemetery: Battleround to Community — Brightwood Heritage Trail,” “Fort Stevens” and “Mayor Emery and the Union Army.” United States: Historical Marker Database, retrieved online May 20, 2025.
- “Battleground to Community: Brightwood Heritage Trail.” Washington, D.C.: Cultural Tourism DC, 2008.
- Burial Ledgers, in Record Group 15, The National Cemetery Administration, and Record Group 92, U.S. Departments of Defense and Army (Quartermaster General). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration: 1861-1865.
- Civil War Muster Rolls, in Records of the Department of Military and Veterans’ Affairs (Record Group 19, Series 19.11). Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission.
- Civil War Veterans’ Card File. Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania State Archives.
- Claims for Widow and Minor Pensions, in U.S. Civil War Widows’ Pension Files. Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- “Florida’s Role in the Civil War,” in “Florida Memory.” Tallahassee, Florida: State Archives of Florida.
- “Grand Military Review: Streets Crowded with Spectators: Sherman Greeted with Deafening Cheers.” Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: The Daily Post, May 25, 1865.
- Historic Pennsylvania Church and Town Records (baptismal, marriage, death and burial records of various churches across Pennsylvania). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Historical Society of Pennsylvania.
- Interment Control Forms, in Record Group 92, U.S. Office of the Quartermaster General. College Park, Maryland: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- “Our Heroes! The Grand Review at Washington. Honor to the Brave. Immense Outpouring of the People. The Troops Reviewed by Gen. Grant.” Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Daily Telegraph, May 23, 1865.
- Pennsylvania Veterans’ Burial Index Cards. Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania Department of Military and Veterans Affairs.
- “Reconstruction: An Overview.” Washington, D.C.: American Battlefield Trust, November 28, 2023.
- Registers of Deaths of Volunteers, in Records of the U.S. Adjutant General’s Office. Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Rodrock, Rev. William D. C. Chaplain’s Reports (47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry, 1865). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Schmidt, Lewis. A Civil War History of the 47th Regiment of Pennsylvania Veteran Volunteers. Allentown, Pennsylvania: Self-published, 1986.
- Steers, Edward Jr. and Harold Holzer. The Lincoln Assassination Conspirators: Their Confinement and Execution, as Recorded in the Letterbook of John Frederick Hartranft. Baton Rouge, Louisiana, 2009.
- Stegall, Joel T. “Salisbury Prison: North Carolina’s Andersonville.” Fayetteville, North Carolina: North Carolina Civil War & Reconstruction History Center, 13 September 2018.
- “The Final March: Grand Review of the Armies.” Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Park Service, retrieved online May 20, 2025.
- “The Grand Review: A Grand Spectacle Witnessed.” Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: The Daily Post, May 24, 1865.
- “The Grand Review: Immense Crowds in Washington: Fine Appearance of the Troops: Their Enthusiastic Reception.” Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania Daily Telegraph, May 24, 1865; and West Chester, Pennsylvania: The Record, May 17, 1865.
- “The Grand Review: The City Crowded with Visitors: Order of Corps, Divisions, Brigades and Regiments.” Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Daily Constitutional Union, May 23, 1865.
- “The History of the Forty-Seventh Regt. P. V.” Allentown, Pennsylvania: The Lehigh Register, 20 July 1870.
- Wharton, Henry D. Letters from the Sunbury Guards. Sunbury, Pennsylvania: Sunbury American, 1861-1868.





You must be logged in to post a comment.