
Soldiers’ and Sailors’ Monument, New Bloomfield, Perry County, Pennsylvania, circa early 1900s (public domain).
Alternate Spellings of Surname: Blain, Blaine
Born in Markelsville, Perry County, Pennsylvania on 21 January 1841, Lewis William Blaine was a son of James G. Blaine and Sarah (Vincent) Blaine, and a brother of Perry County-born siblings: William Allison Blaine (1836-1903), who was born on 25 July 1836 and married Mary Jones (1834-1905), before serving with the 208th Pennsylvania Volunteers during the American Civil War; Josephine Ann Blaine (1838-1910), who was born on 27 April 1838 and later wed and was widowed by George William Kochenderfer (1810-1880), before marrying Daniel Barrick (1827-1895); Amanda Blaine (1843-1856), who was born on 29 May 1843, but died at the age of thirteen in Perry County on 18 August 1856; Jasper Harvey Blaine (1845-1930), who was born on 18 May 1845, also served in the 208th Pennsylvania during the Civil War, and later wed and was widowed by Sophia Seeley (1845-1923), before marrying Ella Fretz (1861-1937); and Charity Blaine (1839-1863), who was born on 2 September 1839 and died on 7 August 1863.
American Civil War
Employed as a shoemaker in Bloomfield, Perry County, Pennsylvania at the dawn of the American Civil War, nineteen-year-old Lewis Blaine mustered in for military service as a private with Company D of the newly-formed 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry at Camp Curtin in Harrisburg, Dauphin County, Pennsylvania on 16 September 1861.
Following a brief training period in light infantry tactics, Private Lewis Blaine and his company were sent by train with the 47th Pennsylvania to Washington, D.C. where they were stationed at “Camp Kalorama” on the Kalorama Heights near Georgetown, about two miles from the White House, beginning 20 September. Two days later, C Company Musician Henry D. Wharton penned these words to his hometown newspaper, the Sunbury American:
After a tedious ride we have, at last, arrived at the City of ‘magnificent distances.’ We left Harrisburg on Friday last at 1 o’clock A.M. and reached this camp yesterday (Saturday) at 4 P.M., as tired and worn out a setting [sic, set] of mortals as can possibly exist. On arriving at Washington we were marched to the ‘Soldiers Retreat,’ a building purposefully erected for the benefit of the soldier, where every comfort is extended to him and the wants of the ‘inner man’ supplied.
After partaking of refreshments we were ordered into line and marched, about three miles, to this camp. So tired were the men that, on marching out, some gave out, and had to leave the ranks, but J. Boulton Young, our ‘little Zouave,’ stood it bravely, and acted like a veteran. So small a drummer is scarcely seen in the army, and on the march through Washington he was twice the recipient of three cheers.
We were reviewed by Gen. McClellan yesterday [21 September] without our knowing it. All along the march we noticed a considerable number of officers, both mounted and on foot; the horse of one of the officers was so beautiful that he was noticed by the whole regiment, in fact, so adapt [sic, wrapped] up were they in the horse, the rider wasn’t noticed, and the boys were considerably mortified this morning on discovering they had missed the sight of, and the neglect of not saluting the soldier next in command to Gen. Scott.
Col. Good, who has command of our regiment, is an excellent man and a splendid soldier. He is a man of very few words, and is continually attending to his duties and the wants of the Regiment.
…. Our Regiment will now be put to hard work; such as drilling and the usual business of camp life, and the boys expect and hope for an occasional ‘pop’ at the enemy.

Chain Bridge across the Potomac above Georgetown looking toward Virginia, 1861 (The Illustrated London News, public domain).
Acclimated somewhat to their new life, the soldiers of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry subsequently became part of the Army of the United States when they were officially mustered into federal service on 24 September. Three days later, they were assigned to the 3rd Brigade of Brigadier-General Isaac Ingalls Stevens, which also included the 33rd, 49th and 79th New York regiments. By that afternoon, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were on the move again.
Ordered onward by Brigadier-General Silas Casey, the Mississippi rifle-armed 47th Pennsylvania infantrymen marched behind their Regimental Band until reaching Camp Lyon, Maryland on the Potomac River’s eastern shore. At 5 p.m., they joined the 46th Pennsylvania in moving double-quick (one hundred and sixty five steps per minute using thirty-three-inch steps) across the “Chain Bridge” marked on federal maps, and continued on for roughly another mile before being ordered to make camp.
The next morning, they broke camp and moved again. Marching toward Falls Church, Virginia, they arrived at Camp Advance around dusk. There, about two miles from the bridge they had crossed a day earlier, they re-pitched their tents in a deep ravine near a new federal fort under construction (Fort Ethan Allen). They had completed a roughly eight-mile trek, were situated close to the headquarters of Brigadier-General William Farrar Smith (also known as “Baldy”) and were now part of the massive U.S. Army of the Potomac (“Mr. Lincoln’s Army”). Under Smith’s leadership, their regiment and brigade would help to defend the nation’s capital from the time of their arrival through late January when the men of the 47th Pennsylvania would be shipped south.
Once again, Company C Musician Henry Wharton recalled the regiment’s activities, noting, via his 29 September letter to the Sunbury American:
On Friday last we left Camp Kalorama, and the same night encamped about one mile from the Chain Bridge on the opposite side of the Potomac from Washington. The next morning, Saturday, we were ordered to this camp [Camp Advance near Fort Ethan Allen, Virginia], one and a half miles from the one we occupied the night previous. I should have mentioned that we halted on a high hill (on our march here) at the Chain Bridge, called Camp Lyon, but were immediately ordered on this side of the river. On the route from Kalorama we were for two hours exposed to the hardest rain I ever experienced. Whew, it was a whopper; but the fellows stood it well – not a murmur – and they waited in their wet clothes until nine o’clock at night for their supper. Our Camp adjoins that of the N.Y. 79th (Highlanders.)….
We had not been in this Camp more than six hours before our boys were supplied with twenty rounds of ball and cartridge, and ordered to march and meet the enemy; they were out all night and got back to Camp at nine o’clock this morning, without having a fight. They are now in their tents taking a snooze preparatory to another march the morning…. I don’t know how long the boys will be gone, but the orders are to cook two days’ rations and take it with them in their haversacks….
There was a nice little affair came off at Lavensville [sic, Lewinsville], a few miles from here on Wednesday last; our troops surprised a party of rebels (much larger than our own.) killing ten, took a Major prisoner, and captured a large number of horses, sheep and cattle, besides a large quantity of corn and potatoes, and about ninety six tons of hay. A nice day’s work. The boys are well, in fact, there is no sickness of any consequence at all in our Regiment….

The Big Chestnut Tree, Camp Griffin, Langley, Virginia, 1861 (U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Sometime during this phase of duty, as part of the 3rd Brigade, the 47th Pennsylvanians were moved to a site they initially christened “Camp Big Chestnut,” in reference to a large chestnut tree growing there. The site would eventually become known to them as “Camp Griffin,” and was located roughly ten miles from Washington, D.C.
On 11 October, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers marched in the Grand Review at Bailey’s Cross Roads. In a mid-October letter to his own family and friends, Captain John Peter Shindel Gobin, the commanding officer of Company C, reported that Companies D, A, C, F, and I (the 47th Pennsylvania’s right wing) were ordered to picket duty after the regiment’s left-wing companies (B, E, G, H, and K) had been forced to return to camp by Confederate troops.
In his letter of 13 October, Musician Henry Wharton described the duties of the average 47th Pennsylvanian, as well as the regiment’s new home:
The location of our new camp is fine and the scenery would be splendid if the view was not obstructed by heavy thickets of pine and innumerable chesnut [sic, chestnut] trees. The country around us is excellent for the Rebel scouts to display their bravery; that is, to lurk in the dense woods and pick off one of our unsuspecting pickets. Last night, however, they (the Rebels) calculated wide of their mark; some of the New York 33d boys were out on picket; some fourteen or fifteen shots were exchanged, when our side succeeded in bringing to the dust, (or rather mud,) an officer and two privates of the enemy’s mounted pickets. The officer was shot by a Lieutenant in Company H [?], of the 33d.
Our own boys have seen hard service since we have been on the ‘sacred soil.’ One day and night on picket, next day working on entrenchments at the Fort (Ethan Allen.) another on guard, next on march and so on continually, but the hardest was on picket from last Thursday morning ’till Saturday morning – all the time four miles from camp, and both of the nights the rain poured in torrents, so much so that their clothes were completely saturated with the rain. They stood it nobly – not one complaining; but from the size of their haversacks on their return, it is no wonder that they were satisfied and are so eager to go again tomorrow. I heard one of them say ‘there was such nice cabbage, sweet and Irish potatoes, turnips, &c., out where their duty called them, and then there was a likelihood of a Rebel sheep or young porker advancing over our lines and then he could take take them as ‘contraband’ and have them for his own use.’ When they were out they saw about a dozen of the Rebel cavalry and would have had a bout with them, had it not been for … unlucky circumstance – one of the men caught the hammer of his rifle in the strap of his knapsack and caused his gun to fire; the Rebels heard the report and scampered in quick time….
On Friday morning, 22 October 1861, the 47th engaged in a divisional review, described by historian Lewis Schmidt as massing “about 10,000 infantry, 1000 cavalry, and twenty pieces of artillery all in one big open field.” On 21 November, the 47th participated in a morning divisional headquarters review that was monitored by the regiment’s founder and commanding officer, Colonel Tilghman H. Good — a formal inspection that was followed by brigade and division drills all afternoon. According to Schmidt, “each man was supplied with ten blank cartridges.” Afterward, “Gen. Smith requested Gen. Brannan to inform Col. Good that the 47th was the best regiment in the whole division.”
As a reward — and in preparation for bigger things to come, Brigadier-General John Milton Brannan obtained new Springfield rifles for every member of the 47th Pennsylvania.
1862

The City of Richmond, a sidewheel steamer, transported Union troops during the Civil War (Maine, circa late 1860s, public domain).
Ordered to move from their Virginia encampment back to Maryland, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers left Camp Griffin at 8:30 a.m. on Wednesday, 22 January 1862. Marching through deep mud with their equipment for three miles in order to reach the railroad station at Falls Church, they were transported to Alexandria, where they boarded the steamship City of Richmond and sailed the Potomac River to the Washington Arsenal, where they disembarked and were re-equipped. Subsequently marched to the Soldiers’ Rest in Washington, D.C., they were fed and given the opportunity to relax there. The next afternoon, they were marched to the railroad station, where they hopped aboard a train from the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad, and headed for Annapolis, Maryland.
Arriving around 10 p.m., they disembarked and were marched to a barracks at the United States Naval Academy, where they bedded down for the night. They then spent that Friday through Monday (24-27 January) loading their equipment and supplies onto the U.S.S. Oriental.
During the afternoon of 27 January, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers began boarding the Oriental, enlisted men first, and then, per the directive of Brigadier-General Brannan, they steamed away at 4 p.m. and headed for Florida, which, despite its secession from the United States remained strategically important to the Union due to the presence of several key federal installations.

Lighthouse, Key West, Florida, early to mid-1800s (Florida for Tourists, Invalids, and Settlers, George M. Barbour, 1881, public domain).
Arriving in Key West, Florida by early February 1862, the men of Company D and their fellow 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers disembarked and were ordered to pitch their tents on the beach, where they rested and were subsequently directed to their respective quarters inside and outside of Fort Taylor. Assigned to garrison the fort, they drilled daily in infantry and artillery tactics, began strengthening the fortifications of this key federal installation and also began making infrastructure improvements to the city by felling trees and building new roads.
During the weekend of 14 February, the regiment introduced itself to area residents via a parade through the city’s streets. That Sunday, the 47th Pennsylvanians began mingling with locals at area church services.
Among the lighter moments, the regiment commemorated the birthday of President George Washington with a parade, a special ceremony involving the reading of Washington’s farewell address to the nation (first delivered in 1796), the firing of cannon at the fort, and a sack race and other games on 22 February. The festivities resumed two days later when the Regimental Band hosted an officers’ ball at which “all parties enjoyed themselves, for three o’clock of the morning sounded on their ears before any motion was made to move homewards,” according to Musician Henry Wharton. This was then followed by a concert by the regimental band on Wednesday evening, 26 February.
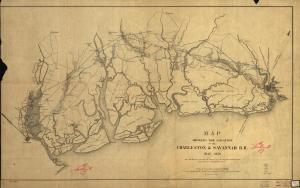
This 1856 map of the Charleston & Savannah Railroad shows the island of Hilton Head, South Carolina in relation to the towns of Beaufort and Pocotaligo (U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Next ordered to Hilton Head, South Carolina, from early June through July, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers camped near Fort Walker before relocating roughly thirty-five miles away in the Beaufort District in the U.S. Army’s Department of the South. Frequently assigned to hazardous picket duty north of their main camp, they faced an increased risk of enemy sniper fire. Despite this danger, though, the men of the 47th Pennsylvania “received the highest commendation from Generals Hunter and Brannan” for their “attention to duty, discipline and soldierly bearing,” according to historian Samuel P. Bates.
Detachments from the regiment were also assigned to the Expedition to Fenwick Island (9 July) and the Demonstration against Pocotaligo (10 July).
Capture of Saint John’s Bluff, Florida and a Confederate Steamer

Earthworks surrounding the Confederate battery atop Saint John’s Bluff along the Saint John’s River in Florida (J. H. Schell, 1862, public domain).
During a return expedition to Florida, beginning 30 September, the 47th Pennsylvania joined with the 1st Connecticut Battery, 7th Connecticut Infantry and part of the 1st Massachusetts Cavalry in assaulting Confederate forces at their heavily protected camp at Saint John’s Bluff, overlooking the Saint John’s River. Trekking through roughly twenty-five miles of swampland and forests, after disembarking from their Union troop transports at Mayport Mills on 1 October, the 47th Pennsylvanians captured artillery and ammunition stores (on 3 October) that had been abandoned during the Union Navy’s bombardment of the bluff.
Men from the 47th Pennsylvania’s Companies E and K were then led by Captain Charles H. Yard on a special mission; initially joining with other Union troops in the reconnaissance and capture of Jacksonville, Florida, they were subsequently ordered to sail up the Saint John’s River to seek out and capture any Confederate ships they found. Departing aboard the Darlington, a former Confederate steamer, with protection by the Union gunboat Hale, they traveled two hundred miles upriver, captured the Governor Milton, a Confederate steamer that was docked near Hawkinsville, and returned back down the river with both Union ships and their new Confederate prize without incident. (Identified as a thorn that needed to be plucked from the Union’s side, that steamer had been engaged in ferrying Confederate troops and supplies around the region.)
Integration of the Regiment
Meanwhile, back at its South Carolina base of operations, the 47th Pennsylvania was making history as it became an integrated regiment. On 5 and 15 October, the regiment added to its rosters several young Black men who had endured plantation enslavement near Beaufort and other areas of South Carolina, including Bristor Gethers, Abraham Jassum and Edward Jassum.
Battle of Pocotaligo, South Carolina

Highlighted version of the U.S. Army map of the Coosawhatchie-Pocotaligo Expedition, 22 October 1862 (public domain).
From 21-23 October 1862, under the brigade and regimental commands of Colonel Tilghman Good and Lieutenant-Colonel George Warren Alexander, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers joined with other Union troops in engaging heavily protected Confederate troops in and around Pocotaligo, South Carolina, including at Frampton’s Plantation and the Pocotaligo Bridge, a key piece of Deep South infrastructure that senior Union military leaders felt should be eliminated.
Harried by snipers while en route to destroy the bridge, they met resistance from an entrenched, heavily fortified Confederate battery that opened fire on the Union troops as they entered an open cotton field.
Those headed toward higher ground at the Frampton Plantation fared no better as they encountered artillery and infantry fire from the surrounding forests. But the Union soldiers would not give in. Grappling with the Confederates where they found them, they pursued the Rebels for four miles as the Confederate Army retreated to the bridge. Once there, the 47th Pennsylvania relieved the 7th Connecticut.
Unfortunately, the enemy was just too well armed. After two hours of intense fighting in an attempt to take the ravine and bridge, the 47th Pennsylvanians were forced by depleted ammunition to withdraw to Mackay’s Point.
Losses for the 47th were significant. Two officers and eighteen enlisted men died; two officers and an additional one hundred and fourteen enlisted men were wounded.
Badly battered when they returned to Hilton Head on 23 October, a number of 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were subsequently selected to serve as the funeral honor guard for General Ormsby MacKnight Mitchel, the commander of the U.S. Army’s 10th Corps and Department of the South who had succumbed to yellow fever on 30 October. The Mountains of Mitchel, a part of Mars’ South Pole discovered by Mitchel in 1846 while working as a University of Cincinnati astronomer, and Mitchelville, the first Freedmen’s town created after the Civil War, were both later named for him. Men from the 47th Pennsylvania were given the honor of firing the salute over his grave.

Fort Jefferson and its wharf areas, Dry Tortugas, Florida (Harper’s Weekly, 23 February 1861, public domain).
Having been ordered back to Key West on 15 November 1862, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers would spend much of 1863 guarding federal installations in Florida as part of the 10th Corps, Department of the South. Companies A, B, C, E, G, and I would once again garrison Fort Taylor in Key West, while the men of Companies D, F, H, and K would garrison Fort Jefferson, the Union’s remote outpost in the Dry Tortugas off the southern coast of Florida.
After packing their belongings at their Beaufort, South Carolina encampment and loading their equipment onto the U.S. Steamer Cosmopolitan, the officers and enlisted members of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry sailed toward the mouth of the Broad River on 15 December 1862, and anchored briefly at Port Royal Harbor in order to allow the regiment’s medical director, Elisha W. Baily, M.D., and members of the regiment who had recuperated enough from their Pocotaligo-related battle injuries at the Union’s general hospital at Hilton Head, to rejoin the regiment.
At 5 p.m. that same evening, the regiment sailed for Florida, during what was described by several members of the regiment as a treacherous and nerve-wracking voyage. According to Schmidt, the ship’s captain “steered a course along the coast of Florida for most of the voyage,” which made the voyage more precarious “because of all the reefs.” On 16 December, “the second night, the ship was jarred as it ran aground on one during a storm, but broke free, and finally steered a course further from shore, out in the Gulf Stream.”
In a letter penned to the Sunbury American on 21 December, Musician Henry Wharton provided the following details about the regiment’s trip:
On the passage down, we ran along almost the whole coast of Florida. Rather all dangerous ground, and the reefs are no playthings. We we jarred considerably by running on one, and not liking the sensation our course was altered for the Gulf Stream. We had heavy sea all the time. I had often heard of ‘waves as big as a house,’ and thought it was a sailors yarn, but I have seen ’em and am perfectly satisfied; so now, not having a nautical turn of mind, I prefer our movements being done on terra firma, and leave old neptune to those who have more desire for his better acquaintance. A nearer chance of a shipwreck never took place than ours, and it was only through Providence that we were saved. The Cosmopolitan is a good riverboat, but to send her to sea, loadened [sic, loaded] with U.S. troops is a shame, and looks as though those in authority wish to get clear of soldiers in another way than that of battle. There was some sea sickness on our passage; several of the boys ‘casting up their accounts’ on the wrong side of the ledger.
According to Corporal George Nichols of Company E, “When we got to Key West the Steamer had Six foot of water in her hole [sic, hold]. Waves Mountain High and nothing but an old river Steamer. With Eleven hundred Men on I looked for her to go to the Bottom Every Minute.”
Although the Cosmopolitan arrived at the Key West Harbor on Thursday, 18 December, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers did not set foot on Florida soil until noon the next day. The men from Companies C and I were immediately marched to Fort Taylor, where they were placed under the command of Major William Gausler, the regiment’s third-in-command. The men from Companies B and E were assigned to the older barracks that had been erected by the United States Army, and were placed under the command of B Company Captain Emanuel P. Rhoads, while the men from Companies A and G were placed under the command of A Company Captain Richard Graeffe, and stationed at newer facilities known as the “Lighthouse Barracks,” which were located on “Lighthouse Key.”
On Saturday, 21 December, Lieutenant-Colonel George W. Alexander, the regiment’s second-in-command, sailed away aboard the Cosmopolitan with the men from Companies D, F, H, and K, and headed south to Fort Jefferson, roughly seventy miles off the coast of Florida (in the Gulf of Mexico) to assume garrison duties there. According to Musician Henry Wharton:
We landed here [Fort Taylor] on last Thursday at noon, and immediately marched to quarters. Company I. and C., in Fort Taylor, Company E. and B. in the old Barracks, and A. and G. in the new Barracks. Lieut. Col. Alexander, with the other four companies proceeded to Tortugas, Col. Good having command of all the forces in and around Key West. Our regiment relieved the 90th Regiment N. Y. S. Vols. Col. Joseph Morgan, who will proceed to Hilton Head to report to the General commanding. His actions have been severely criticized by the people, but, as it is in bad taste to say anything against ones [sic, one’s] superiors, I merely mention, judging from the expression of the citizens, they were very glad of the return of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers….
Key West has improved very little since we left last June, but there is one improvement for which the 90th New York deserve a great deal of praise, and that is the beautifying of the ‘home’ of dec’d soldiers. A neat and strong wall of stone encloses the yard, the ground is laid off in squares, all the graves are flat and are nicely put in proper shape by boards eight or ten inches high on the end sides, covered with white sand, while a head and foot board, with the full name, company and regiment, marks the last resting place of the patriot who sacrificed himself for his country….
1863

Fort Jefferson’s moat and wall, circa 1934, Dry Tortugas, Florida (C. E. Peterson, U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Although water quality was a challenge for members of the regiment at both of their duty stations in Florida throughout 1863, it was particularly problematic for the 47th Pennsylvanians who were stationed at Fort Jefferson. According to Schmidt:
‘Fresh’ water was provided by channeling the rains from the city’s barbette through channels in the interior walls, to filter trays filled with sand; and finally to the 114 cisterns located under the fort which held, 1,231,000 gallons of water. The cisterns were accessible in each of the first level cells or rooms through a ‘trap hole’ in the floor covered by a temporary wooden cover…. Considerable dirt must have found its way into these access points and was responsible for some of the problems resulting in the water’s impurity…. The fort began to settle and the asphalt covering on the outer walls began to deteriorate and allow the sea water (polluted by debris in the moat) to penetrate the system…. Two steam condensers were available … and distilled 7000 gallons of tepid water per day for a separate system of reservoirs located in the northern section of the parade ground near the officers [sic, officers’] quarters. No provisions were made to use any of this water for personal hygiene of the [planned 1,500-soldier garrison force]….
As a result, the soldiers stationed there washed themselves and their clothes, using saltwater from the ocean. As if that weren’t difficult enough, “toilet facilities were located outside of the fort,” according to Schmidt:
At least one location was near the wharf and sallyport, and another was reached through a door-sized hole in a gunport and a walk across the moat on planks at the northwest wall…. These toilets were flushed twice each day by the actions of the tides, a procedure that did not work very well and contributed to the spread of disease. It was intended that the tidal flush should move the wastes into the moat, and from there, by similar tidal action, into the sea. But since the moat surrounding the fort was used clandestinely by the troops to dispose of litter and other wastes … it was a continuous problem for Col. Alexander and his surgeon.

Second-tier casemates, lighthouse keeper’s house, sallyport, and lean-to structure, Fort Jefferson, Dry Tortugas, Florida, late 1860s (U.S. National Park Service and National Archives, public domain).
As for daily operations in the Dry Tortugas, there was a fort post office and the “interior parade grounds, with numerous trees and shrubs in evidence, contained officers’ quarters, [a] magazine, kitchens and out houses,” per Schmidt, as well as “a ‘hot shot oven’ which was completed in 1863 and used to heat shot before firing.”
Most quarters for the garrison … were established in wooden sheds and tents inside the parade [grounds] or inside the walls of the fort in second-tier gun rooms of ‘East’ front no. 2, and adjacent bastions … with prisoners housed in isolated sections of the first and second tiers of the southeast, or no. 3 front, and bastions C and D, located in the general area of the sallyport. The bakery was located in the lower tier of the northwest bastion ‘F’, located near the central kitchen….
Additional Duties: Diminishing Florida’s Role as the “Supplier of the Confederacy”
On top of the strategic role played by the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers in preventing foreign powers from assisting the Confederate Army and Navy in gaining control over federal forts in the Deep South, the regiment was also called upon to play an ongoing role in weakening Florida’s abilities to supply and transport food and troops throughout areas held by the Confederate States of America.
Prior to intervention by the Union Army and Navy, the owners of plantations and livestock ranches, as well as the operators of small, family farms across Florida, had been able to consistently furnish beef and pork, fish, fruits, and vegetables to Confederate troops stationed throughout the Deep South during the first year of the American Civil War. Large herds of cattle were raised near Fort Myers, for example, while orchard owners in the Saint John’s River area were actively engaged in cultivating sizeable orange groves (while other types of citrus trees were found growing throughout more rural areas of the state).
Florida was also a major producer of salt, which was used as a preservative for food. As a result, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers and other Union troops across Florida were ordered to capture or destroy salt manufacturing facilities in order to further curtail the enemy’s access to food.
But they were undertaking all of these duties in conditions that were far more challenging than any they had previously faced (and that were far more challenging than what many other Union troops were facing up north). The weather was frequently hot and humid as spring turned to summer, mosquitos and other insects were an ever-present annoyance (and serious threat when they were carrying tropical diseases) and there were also scorpions and snakes that put the men’s health at further risk.
As part of their efforts to ensure the efficacy of their ongoing operations, regimental officers periodically tweaked the assignments of individual companies during that year of garrison duty. One of those changes occurred on 16 May 1863 when D Company Captain Henry D. Woodruff and his men marched to the wharf at Fort Jefferson and climbed aboard yet another ship — this time for their return to Fort Taylor in Key West, where they resumed garrison duties under the command of Colonel Tilghman H. Good.
Four days later, enlisted members of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry were finally given eight months’ worth of their back pay — a significant percentage of which was quickly sent home to family members who had been struggling to make ends meet.
But there was more heartache to come. As the days of summer began to fade, Private Lewis Blaine received sad news from home. His sister, Charity Blaine, had died in Perry County on 7 August 1863.
Despite all of these hardships, when members of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry were offered the opportunity to re-enlist during the fall of 1863, more than half of the regiment’s personnel did so without hesitation. Among those choosing to re-up for an additional tour of duty was Private Lewis Blaine, who re-enlisted as a private with the same regiment and company at Fort Taylor in Key West on 10 October 1863.
1864
In early January 1864, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers experienced yet another significant change when members of the regiment were ordered to expand the Union’s reach by sending part of the regiment north to retake possession of Fort Myers, a federal installation that had been abandoned in 1858, following the federal government’s third war with the Seminole Indians. In response, A Company Captain Richard Graeffe and a group of soldiers from Company A traveled north, captured the fort and began conducting cattle raids to provide food for the growing Union troop presence across Florida. They subsequently turned the fort not only into their base of operations, but into a shelter for pro-union supporters, escaped slaves, Confederate deserters, and others fleeing Rebel troops.
Red River Campaign
Meanwhile, all of the other companies of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry had begun preparing for the regiment’s history-making journey to Louisiana. Boarding yet another steamer, the Charles Thomas, the men from Companies B, C, D, I, and K headed for Algiers, Louisiana (across the river from New Orleans), followed on 1 March by the men from Companies E, F, G, and H.
Upon the second group’s arrival, the now almost-fully-reunited regiment moved by train to Brashear City (now Morgan City, Louisiana) before heading to Franklin by steamer through the Bayou Teche. There, the 47th Pennsylvania Infantry joined the 2nd Brigade, 1st Division of the Department of the Gulf’s 19th Army Corps (XIX Corps), and became the only Pennsylvania regiment to serve in the Red River Campaign of Union Major-General Nathaniel P. Banks. (Unable to reach Louisiana until 23 March, the soldiers from Company A were assigned to detached duty while awaiting transport that enabled them to reconnect with their regiment at Alexandria, Louisiana on 9 April).
From 14-26 March, the 47th passed through New Iberia, Vermilionville (now part of Lafayette), Opelousas, and Washington while en route to Alexandria and Natchitoches. Often short on food and water, the regiment encamped briefly at Pleasant Hill the night of 7 April before continuing on the next day, marching until mid-afternoon.
Rushed into battle ahead of other regiments in the 2nd Division, sixty members of the 47th were cut down on 8 April during the volley of fire unleashed during the Battle of Sabine Cross Roads. The fighting waned only when darkness fell. Exhausted, those who were uninjured collapsed between the bodies of the gravely wounded and dead. After midnight, the surviving Union troops withdrew to Pleasant Hill.
The next day, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were ordered into a critically important defensive position at the far right of the Union lines, their right flank spreading up onto a high bluff. By 3 p.m., after enduring a midday charge by the troops of Confederate Major-General Richard Taylor (a plantation owner and son of Zachary Taylor, former president of the United States), the brutal fighting still showed no signs of ending. Suddenly, just as the 47th was shifting to the left side of the massed Union forces, the men of the 47th Pennsylvania were forced to bolster the 165th New York’s buckling lines by blocking another Confederate assault during what has since become known as the Battle of Pleasant Hill.
Once again, casualties were severe. And this time, the roster included the names of multiple members of Company D, including Private Ephraim Clouser, who was listed among the wounded and missing. Shot in the right knee by a Confederate rifle, he and multiple other 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantrymen had been captured by Rebel troops and marched roughly one hundred and twenty-five miles southwest to Camp Ford, the largest Confederate States prison camp west of the Mississippi River.
* Note: Located in Smith County, Texas, near the town of Tyler, that prisoner of war camp has been portrayed by some historians as far less dangerous of a place of captivity for Union soldiers than Andersonville and other Confederate prisons because its living conditions were reportedly “better” than the conditions found at those infamous POW camps — theoretically because the number of POWs held at Camp Ford was smaller and, therefore, “more easily cared for.” But as Camp Ford’s POW population skyrocketed in 1864, fueled by the capture of thousands of Union soldiers during multiple Red River Campaign battles, those living conditions quickly deteriorated.
As food, safe drinking water and adequate shelter became increasingly scarce, more and more of the Union soldiers confined there grew weak from starvation, fell ill and died due to the spread of typhoid and other infectious diseases, as well as the cases of dysentery and chronic diarrhea that were caused by the unsanitary placement of outdoor latrines near the camp’s water source.
On 12 June 1864, Private Samuel Kern, a D Company comrade of Private Clouser who had also been captured at Pleasant Hill, became one of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers who died at Camp Ford. Buried somewhere on the camp’s grounds, his precise final resting place remains unknown.
Four days later, Private Ephraim Clouser was reportedly one of a group of Union POWs who were being paroled at Red River Landing, Louisiana (on 16 June 1864, as part of a prisoner exchange agreement between the armies of United States and Confederate States). But that report turned out to be a false one. Private Clouser was actually being held back from release by his Camp Ford captors — for a reason which has yet to be identified by researchers. (Forced to languish there as a POW for an additional five months, during which time he was at increasing risk of starvation, physical and mental illness, or death, he was finally released to the Union Army on 25 November 1864.)
Meanwhile, as the captured 47th Pennsylvanians were being spirited away to Camp Ford, Private Lewis Blaine and the bulk of his regiment were carrying out orders from senior Union Army leaders to head for Grand Ecore, Louisiana. Encamped there from 11-22 April, they engaged in the hard labor of strengthening regimental and brigade fortifications.
They then moved back to Natchitoches Parish on 22 April. While en route, they were attacked again, this time, at the rear of their retreating brigade, but they were able to end the encounter quickly and move on to reach Cloutierville at 10 p.m. that same night (after a forty-five-mile march).
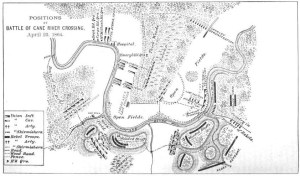
The 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were stationed just to the left of the “Thick Woods” with Emory’s 2nd Brigade, 1st Division as shown on this map of Union troop positions for the Battle of Cane River Crossing at Monett’s Ferry, Louisiana, 23 April 1864 (Major-General Nathaniel Banks’ official Red River Campaign Report, public domain).
The next morning (23 April), episodic skirmishing quickly roared into the flames of a robust fight. As part of the advance party led by Union Brigadier-General William Emory, the 47th Pennsylvanians took on the Confederate cavalry of Brigadier-General Hamilton P. Bee in the Battle of Cane River (also known as “the Affair at Monett’s Ferry” or the “Cane River Crossing”).
Responding to a barrage from the Confederate artillery’s twenty-pound Parrott guns and raking fire from enemy troops positioned near a bayou and atop a bluff, Brigadier-General Emory directed one of his brigades to keep Bee’s Confederates busy while sending two other brigades to find a safe spot for the Union force to cross the Cane River. As part of the “beekeepers,” the 47th Pennsylvania supported Emory’s artillery.
While all of that action was unfolding, additional troops under Smith’s command, attacked Bee’s flank to force a Rebel retreat, and then erected a series of pontoon bridges that enabled the 47th Pennsylvania and other Union troops to make the Cane River Crossing by the next day. As the Confederates retreated, they torched their own food stores, as well as the cotton supplies of their fellow southerners. In a letter penned from Morganza, C Company’s Henry Wharton described what had happened:
Our sojourn at Grand Ecore was for eleven days, during which time our position was well fortified by entrenchments for a length of five miles, made of heavy logs, five feet high and six feet wide, filled in with dirt. In front of this, trees were felled for a distance of two hundred yards, so that if the enemy attacked we had an open space before us which would enable our forces to repel them and follow if necessary. But our labor seemed to the men as useless, for on the morning of 22d April, the army abandoned these works and started for Alexandria. From our scouts it was ascertained that the enemy had passed some miles to our left with the intention of making a stand against our right at Bayou Cane, where there is a high bluff and dense woods, and at the same attack Smith’s forces who were bringing up the rear. This first day was a hard one on the boys, for at 10 o’clock at night they made Cloutierville, a distance of forty-five miles. On that day the rear was attacked which caused our forces to reverse their front and form in line of battle, expecting too, to go back to the relief of Smith, but he needed no assistance, sending word to the front that he had ‘whipped them, and could do it again.’ It was well that Banks made so long a march on that day, for on the next we found the enemy prepared to carry out their design of attacking us front and rear. Skirmishing commenced early in the morning and as our columns advanced he fell back towards the bayou, when we soon discovered the position of their batteries on the bluff. There was then an artillery duel by the smaller pieces, and some sharp fighting by the cavalry, when the ‘mule battery,’ twenty pound Parrott guns opened a heavy fire, which soon dislodged them, forcing the chivalry to flee in a manner not at all suitable to their boasted courage. Before this one cavalry, the 3d Brigade of the 1st Div., and Birges’ brigade of the second, had crossed the bayou and were doing good service, which, with the other work, made the enemy show their heels. The 3d brigade done some daring deeds in this fight, as also did the cavalry. In one instance the 3d charged up a hill almost perpendicular, driving the enemy back by the bayonet without firing a gun. The woods on this bluff was so thick that the cavalry had to dismount and fight on foot. During the whole of the day, our brigade, the 2d, was supporting artillery, under fire all the time, and could not give Mr. Reb a return shot.
While we were fighting in front, Smith was engaged some miles in the rear, but he done his part well and drove them back. The rebel commanders thought by attacking us in the rear, and having a large face on the bluffs, they would be able to capture our train and take us all prisoners, but in this they were mistaken, for our march was so rapid that we were on them before they had thrown up the necessary earthworks. Besides they underrated the amount of our artillery, calculating from the number engaged at Pleasant Hill. The rebels say ‘it seems as though the Yankees manufacture, on short notice, artillery to order, and the men are furnished with wings when they wish to make a certain point.’
The damage done to the Confederate cause by the burning of cotton was immense. On the night of the 22d our route was lighted up for miles and millions of dollars worth of this production was destroyed. This loss will be felt more by Davis & Co., than several defeats in this region, for the basis of the loan in England was on the cotton in Louisiana.
After the rebels had fled from the bluff the negro troops put down the pontoons, and by ten that night we were six miles beyond the bayou safely encamped. The next morning we moved forward and in two days were in Alexandria. Johnnys followed Smith’s forces, keeping out of range of his guns, except when he had gained the eminence across the bayou, when he punished them (the rebs) severely.

“Passage of the Fleet of Gunboats Over the Falls at Alexandria, Louisiana, May 1864 (Frank Leslie’s Illustrated Newspaper, July 16, 1864, U.S. Library of Congress, public domain; click to enlarge).
Having finally reached Alexandria on 26 April, they learned they would remain at their latest new camp for at least two weeks. Placed temporarily under the command of Lieutenant-Colonel Joseph Bailey, they were assigned yet again to the hard labor of construction work, helping to erect “Bailey’s Dam,” a timber structure that was designed to enable Union Navy gunboats to safely navigate the fluctuating waters of the Red River. According to Wharton:
We were at Alexandria seventeen days, during which time the men were kept busy at throwing up earthworks, foraging and three times went out some distance to meet the enemy, but they did not make their appearance in numbers large enough for an engagement. The water in the Red river had fallen so much that it prevented the gun boats from operating with us, and kept our transports from supplying the troops with rations, (and you know soldiers, like other people will eat), so Banks was compelled to relinquish his designs on Shreveport and fall back to the Mississippi. To do this a large dam had to be built on the falls at Alexandria to get the iron clads down the river. After a great deal of labor this was accomplished and by the morning of May 13th the last one was through the shute [sic, chute], when we bade adieu to Alexandria, marching through the town with banners flying and keeping step to the music of ‘Rally around the flag,’ and ‘When this cruel war is over.’ The next morning, at our camping place, the fleet of boats passed us, when we were informed that Alexandria had been destroyed by fire – the act of a dissatisfied citizen and several negroes. Incendiary acts were strictly forbidden in a general order before we left the place, and a cavalry guard was left in the rear to see the order enforced. After marching a few miles skirmishing commenced in front between the cavalry and the enemy in riflepits on the bank of the river, but they were easily driven away. When we came up we discovered their pits and places where there had been batteries planted. At this point the John Warren, an unarmed transport, on which were sick soldiers and women, was fired into and sunk, killing many and those that were not drowned taken prisoners. A tin-clad gun boat was destroyed at the same place, by which we lost a large mail. Many letters and directed envelopes were found on the bank – thrown there after the contents had been read by the unprincipled scoundrels. The inhumanity of Guerrilla bands in this department is beyond belief, and if one did not know the truth of it or saw some of their barbarities, he would write it down as the story of a ‘reliable gentleman’ or as told by an ‘intelligent contraband.’ Not satisfied with his murderous intent on unarmed transports he fires into the Hospital steamer Laurel Hill, with four hundred sick on board. This boat had the usual hospital signal floating fore and aft, yet, notwithstanding all this, and the customs of war, they fired on them, proving by this act that they are more hardened than the Indians on the frontier.
Continuing their march, Private Lewis Blaine and his fellow 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers headed toward Avoyelles Parish. According to Wharton:
On Sunday, May 15th, we left the river road and took a short route through the woods, saving considerable distance. The windings of the Red river are so numerous that it resembles the tape-worm railroad where with the politicians frightened the dear people during the administration of Ritner and Stevens. – We stopped several hours in the woods to leave cavalry pass, when we moved forward and by four o’clock emerged into a large open plain where we formed in line of battle, expecting a regular engagement. The enemy, however, retired, and we advanced ’till dark, when the forces halted for the night with orders to rest on their arms. – ‘Twas here that Banks rode through our regiment, amidst the cheers of the boys, and gave the pleasant news that Grant had defeated Lee.

“Sleeping on Their Arms” by Winslow Homer (Harper’s Weekly, 21 May 1864).
“Resting on their arms,” (half-dozing, without pitching their tents, and with their rifles right beside them), they were now positioned just outside of Marksville, on the eve of the 16 May 1864 Battle of Mansura, which unfolded as follows, according to Wharton:
Early next morning we marched through Marksville into a prairie nine miles long and six wide where every preparation was made for a fight. The whole of our force was formed in line, in support of artillery in front, who commenced operations on the enemy driving him gradually from the prairie into the woods. As the enemy retreated before the heavy fire of our artillery, they reached Missoula [sic, Mansura], where they formed in column, taking the whole field in an attempt to flank the enemy, but their running qualities were so good that we were foiled. The maneuvring [sic, maneuvering] of the troops was handsomely done, and the movements was [sic, were] one of the finest things of the war. The fight of artillery was a steady one of five miles. The enemy merely stood that they might cover the retreat of their infantry and train under cover of their artillery. Our loss was slight. Of the rebels we could not ascertain correctly, but learned from citizens who had secreted themselves during the fight, that they had many killed and wounded, who threw them into wagons, promiscuously, and drove them off so that we could not learn their casualties. The next day we moved to Simmsport [sic, Simmesport] on the Achafalaya [sic, Atchafalaya] river, where a bridge was made by putting the transports side by side, which enabled the troops and train to pass safely over. – The day before we crossed the rebels attacked Smith, thinking it was but the rear guard, in which they, the graybacks, were awfully cut up, and four hundred prisoners fell into our hands. Our loss in killed and wounded was ninety. This fight was the last one of the expedition. The whole of the force is safe on the Mississippi, gunboats, transports and trains. The 16th and 17th have gone to their old commands.
It is amusing to read the statements of correspondents to papers North, concerning our movements and the losses of the army. I have it from the best source that the Federal loss from Franklin to Mansfield, and from their [sic, there] to this point does not exceed thirty-five hundred in killed, wounded and missing, while that of the rebels is over eight thousand.

Union Army base at Morganza Bend, Louisiana, circa 1863-1865 (U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Continuing on, the surviving members of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry marched for Simmesport and then Morganza, where they made camp again. While encamped there, the nine formerly enslaved Black men who had enlisted with the regiment in Beaufort, South Carolina (October 1862) and Natchitoches, Louisiana (April 1864) were officially mustered into the regiment between 20-24 June 1864.
The regiment then moved on and arrived in New Orleans in late June. On 4 July, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers received orders to return to the East Coast. Three days later, they began loading their men onto ships, a process that unfolded in two stages. Companies A, C, D, E, F, H, and I boarded the U.S. Steamer McClellan on 7 July and steamed away that day, while the members of Companies B, G and K remained behind, awaiting transport. (The latter group subsequently departed aboard the Blackstone, weighing anchor and sailing forth at the end of that month.)
As a result of this twist of fate, Private Lewis Blaine and his fellow “early travelers” had the good fortune to have a memorable encounter with President Abraham Lincoln on 12 July 1864. They then took part in the mid-July Battle of Cool Spring near Snicker’s Gap, Virginia.
Sheridan’s 1864 Shenandoah Valley Campaign

General Crook’s Battle Near Berryville, Virginia, September 3, 1864 (James E. Taylor, public domain).
Attached to the Middle Military Division, Army of the Shenandoah beginning in August, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry was assigned to defensive duties in and around Halltown, Virginia during the opening days of that month, and then engaged in a series of back-and-forth movements over the next several weeks between Halltown, Berryville, Middletown, Charlestown, and Winchester as part of a “mimic war” being waged by the Union forces of Major-General Philip H. Sheridan with those commanded by Confederate Lieutenant-General Jubal Early.
From 3-4 September, Private Lewis Blaine and the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers took on Early’s Confederates again — this time in the Battle of Berryville. But that month also saw the departure of several 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers who had served honorably, including Company D’s Captain Henry Woodruff, First Lieutenant Samuel Auchmuty, Sergeants Henry Heikel and Alex Wilson, and Corporals Cornelius Stewart and Samuel A. M. Reed — many of whom mustered out on 18 September 1864, upon expiration of their respective service terms.
Those members of the 47th who remained on duty were about to engage in their regiment’s greatest moments of valor.
Battles of Opequan and Fisher’s Hill, September 1864
Together with other regiments under the command of Union Major-General Philip H. (“Little Phil”) Sheridan and Brigadier-General William H. Emory, commander of the 19th Corps, the members of Company D and their fellow 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers helped to inflict heavy casualties on Lieutenant-General Jubal Early’s Confederate forces at Opequan (also spelled as “Opequon” and referred to as “Third Winchester”). The battle is still considered by many historians to be one of the most important during Sheridan’s 1864 campaign; the Union’s victory here helped to ensure the reelection of President Abraham Lincoln.
The 47th Pennsylvania’s march toward destiny at Opequan began at 2 a.m. on 19 September 1864 as the regiment left camp and joined up with others in the Union’s 19th Corps. After advancing slowly from Berryville toward Winchester, the 19th Corps became bogged down for several hours by the massive movement of Union troops and supply wagons, enabling Early’s men to dig in. After finally reaching the Opequan Creek, Sheridan’s men came face to face with the Confederate Army commanded by Early. The fighting, which began in earnest at noon, was long and brutal. The Union’s left flank (6th Corps) took a beating from Confederate artillery stationed on high ground.

Victory of Philip Sheridan’s Union Army over Jubal Early’s Confederate forces, Battle of Opequan, 19 September 1864 (Kurz & Allison, circa 1893, U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
Meanwhile, the 47th Pennsylvania and the 19th Corps were directed by Brigadier-General William Emory to attack and pursue Major-General John B. Gordon’s Confederate forces. Some success was achieved, but casualties mounted as another Confederate artillery group opened fire on Union troops trying to cross a clearing. When a nearly fatal gap began to open between the 6th and 19th Corps, Sheridan sent in units led by Brigadier-Generals Emory Upton and David A. Russell. Russell, hit twice — once in the chest, was mortally wounded. The 47th Pennsylvania opened its lines long enough to enable the Union cavalry under William Woods Averell and the foot soldiers of General George Crook to charge the Confederates’ left flank.
Afterward, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were sent out on skirmishing parties before making camp at Cedar Creek. Moving forward, they would continue to distinguish themselves in battle, but would do so without two more of their respected commanders: Colonel Tilghman Good, founder of the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers; and Good’s second-in-command, Lieutenant-Colonel George Alexander, who mustered out from 23-24 September upon the expiration of their respective terms of service.
Fortunately, they were replaced by others equally admired both for their temperament and their front line experience: Second Lieutenant George Stroop, who was promoted to lead Company D, and John Peter Shindel Gobin, Charles W. Abbott and Levi Stuber, who ultimately became the three most senior leaders of the regiment.
Battle of Cedar Creek, October 1864

Alfred Waud’s 1864 sketch, “Surprise at Cedar Creek,” captured the flanking attack on the rear of Union Brigadier-General William Emory’s 19th Corps by Lieutenant-General Jubal Early’s Confederate army, and the subsequent resistance by Emory’s troops from their Union rifle-pit positions, 19 October 1864 (public domain).
It was during the fall of 1864 that Major-General Philip Sheridan began the first of the Union’s true “scorched earth” campaigns, starving the enemy into submission by destroying Virginia’s crops and farming infrastructure. Viewed through today’s lens of history as inhumane, the strategy claimed many innocents—civilians whose lives were cut short by their inability to find food. This same strategy, however, almost certainly contributed to the further turning of the war’s tide in the Union’s favor during the Battle of Cedar Creek on 19 October 1864. Successful throughout most of their engagement with Union forces at Cedar Creek, Early’s Confederate troops began peeling off in ever growing numbers to forage for food, thus enabling the 47th Pennsylvania and others under Sheridan’s command to rally.
From a military standpoint, it was another impressive, but heartrending day. During the morning of 19 October, Early launched a surprise attack directly on Sheridan’s Cedar Creek-encamped forces. Early’s men were able to capture Union weapons while freeing a number of Confederates who had been taken prisoner during previous battles — all while pushing seven Union divisions back. According to Bates:
When the Army of West Virginia, under Crook, was surprised and driven from its works, the Second Brigade, with the Forty-seventh on the right, was thrown into the breach to arrest the retreat…. Scarcely was it in position before the enemy came suddenly upon it, under the cover of fog. The right of the regiment was thrown back until it was almost a semi-circle. The brigade, only fifteen hundred strong, was contending against Gordon’s entire division, and was forced to retire, but, in comparative good order, exposed, as it was, to raking fire. Repeatedly forming, as it was pushed back, and making a stand at every available point, it finally succeeded in checking the enemy’s onset, when General Sheridan suddenly appeared upon the field, who ‘met his crest-fallen, shattered battalions, without a word of reproach, but joyously swinging his cap, shouted to the stragglers, as he road rapidly past them – “Face the other way, boys! We are going back to our camp! We are going to lick them out of their boots!’”

Sheridan Rallying His Troops, Battle of Cedar Creek, Virginia, 19 October 1864 (U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
The Union’s counterattack punched Early’s forces into submission, and the men of the 47th were commended for their heroism by General Stephen Thomas who, in 1892, was awarded the Medal of Honor for his own “distinguished conduct in a desperate hand-to-hand encounter, in which the advance of the enemy was checked” that day. Bates described the 47th’s actions:
When the final grand charge was made, the regiment moved at nearly right angles with the rebel front. The brigade charged gallantly, and the entire line, making a left wheel, came down on his flank, while engaging the Sixth Corps, when he went “whirling up the valley” in confusion. In the pursuit to Fisher’s Hill, the regiment led, and upon its arrival was placed on the skirmish line, where it remained until twelve o’clock noon of the following day. The army was attacked at early dawn…no respite was given to take food until the pursuit was ended.
Once again, the casualties for the 47th were high. Sergeant William Pyers, the C Company man who had so gallantly rescued the flag at Pleasant Hill was cut down and later buried on the battlefield. Corporal Edward Harper of Company D was wounded, but survived, as did Corporal Isaac Baldwin, who had been wounded earlier at Pleasant Hill. Even Perry County resident and Regimental Chaplain William Rodrock of Perry County suffered a near miss as a bullet pierced his cap.
Following these major engagements, the 47th was ordered to Camp Russell near Winchester from November through most of December. On 14 November, Second Lieutenant George Stroop was promoted to the rank of captain.
Rested and somewhat healed, the 47th was then ordered to outpost and railroad guard duties at Camp Fairview in Charlestown, West Virginia five days before Christmas.
1865 — 1866
Still stationed at Camp Fairview in West Virginia as the New Year of 1865 dawned, members of the regiment continued to patrol and guard key Union railroad lines in the vicinity of Charlestown, while other 47th Pennsylvanians chased down Confederate guerrillas who had made repeated attempts to disrupt railroad operations and kill soldiers from other Union regiments.
Assigned in February 1865 to the Provisional Division of the 2nd Brigade of the U.S. Army of the Shenandoah, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers continued to perform their guerrilla-fighting duties until late March, when they were ordered to head back to Washington, D.C., by way of Winchester and Kernstown, Virginia.
Joyous News and Then Tragedy

Spectators gather for the Grand Review of the Armies, 23-24 May 1865, beside the crepe-draped U.S. Capitol, flag at half-staff following the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln (Matthew Brady, U.S. Library of Congress, public domain).
As April 1865 opened, the battles between the Army of the United States and the Confederate States Army intensified, finally reaching the decisive moment when the Confederate troops of General Robert E. Lee surrendered to Union General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox on 9 April.
The long war, it seemed, was finally over. Less than a week later, however, the fragile peace was threatened when an assassin’s bullet ended the life of President Abraham Lincoln. Shot while attending an evening performance of Our American Cousin at Ford’s Theatre on 14 April 1865, he had died from his wound at 7:22 a.m. the next morning.
Shocked, and devastated by the news, which was received at their Fort Stevens encampment, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were given little time to mourn their beloved commander-in-chief before they were ordered to grab their weapons and move into the regiment’s assigned position, from which it helped to protect the nation’s capital and thwart any attempt by Confederate soldiers and their sympathizers to re-ignite the flames of civil war that had finally been stamped out.
So key was their assignment that the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were not even allowed to march in the funeral procession of their slain leader. Instead, they took part in a memorial service with other members of their brigade that was officiated by the 47th Pennsylvania’s regimental chaplain, the Reverend William D. C. Rodrock.
Present-day researchers who read letters sent by 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers to family and friends back home in Pennsylvania during this period, or post-war interviews conducted by newspaper reporters with veterans of the regiment in later years, will learn that the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were collectively heartbroken by Lincoln’s death and deeply angry at those whose actions had culminated in his murder. Researchers will also learn that at least one member of the regiment, C Company Drummer Samuel Hunter Pyers, was given the high honor of guarding President Lincoln’s funeral train, while other members of the regiment were assigned to guard duty at the prison where the key assassination conspirators were being held during the early days of their imprisonment and trial, which began on 9 May 1865. The regiment was headquartered at Camp Brightwood during this period.
Attached to Dwight’s Division of the 2nd Brigade of the Department of Washington’s 22nd Corps, the 47th Pennsylvania Volunteers were permitted to march in the Union’s Grand Review of the National Armies, which took place in Washington, D.C. on 23 May.
Reconstruction

Ruins of Charleston, South Carolina as seen from the Circular Church, 1865 (U.S. National Archives and Records Administration, public domain).
Afterward, Private Lewis Blaine and his fellow 47th Pennsylvanians were ordered to America’s Deep South. Stationed in Savannah, Georgia in early June, they were assigned again to Dwight’s Division, but this time, they were attached to the 3rd Brigade, U.S. Department of the South.
Subsequently ordered to relieve the 165th New York Volunteers in Charleston, South Carolina in July 1865, they were quartered in the former mansion of the Confederate Secretary of the Treasury.
Beginning on Christmas day of that same year, the majority of 47th Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantrymen, including Private Lewis Blaine, began to honorably muster out in Charleston — a process which continued through early January 1866.
Following a stormy voyage home, the 47th Pennsylvanians disembarked in New York City and were then transported to Philadelphia by train where, at Camp Cadwalader on 9 January 1866, they were officially given their honorable discharge papers.
According to regimental records, Private Blaine’s military clothing account was last settled on New Year’s Eve in December 1864. He had been paid a total of two hundred and sixty-two dollars in bounty, by the time of the regiment’s muster-out on Christmas day in 1865, but was still due to be paid an additional one hundred and forty dollars in bounty; however, he still owed six dollars to the federal government for “arms and acoutrements” and three dollars to the sutler for supplies he had purchased while in service to the nation.
Return to Civilian Life
Following his honorable discharge from the military, Lewis Blaine returned home to Perry County, Pennsylvania, where he promptly wed Eliza J. Smith (1844-1911) and then migrated west with her sometime after 24 August 1868 (the date on which he filed his U.S. Civil War Pension paperwork from Pennsylvania).
The young couple subsequently began to forge a new life together in Shelby County, Iowa, as they welcomed the births of: Anna M. Blaine (1871-1904), who was born in Iowa on 5 May 1871, grew up to become a teacher and later wed and was widowed by Thomas Moler (1871-1895), before marrying James Woods (1863-1923); William Edgar Blaine (1876-1960), who was born in 1876 and later wed Pearle E. Carter (1880-1963); and Sadie Lenore Blaine (1878-1957), who was born in Kirkman, Shelby County on 6 July 1878, was known to family and friends as “Nora” and later wed Isaac B. Ferry (1874-1951).
According to The News of Newport, Pennsylvania, Lewis Blaine went on to become “one of the most prosperous and highly respected farmers of Shelby County.” His wife, Eliza, was one of the founding members of the Kirkman Methodist Episcopal Church.
The Shelby County town where they resided — Kirkman — existed prior to 1880, but was not officially incorporated until 1895. According to historian Edward S. White’s 1915 description of the town:
The coming of the Chicago & Northwestern Railroad laid the foundation of Kirkman. For a good many years it was the terminus of the Carroll branch of the Northwestern, the distance intervening between it and Harlan being covered by a hack [a horse-drawn carriage], which carried the mail and passengers, Snyder Brothers and C. M. Downey running it for the greater part of the time. Located in the valley of a tributary of the Botna river, a valley as fertile as can well be imagined, farmed by good farmers, Kirkman has enjoyed a good trade. It has a good bank, meeting the needs of local business, and two railroads afford ample shipping facilities. Kirkman has the distinction, rather rare for a town of her size, of owning a good system of waterworks.
On October 22, 1880, Albert Keep, trustee, platted a part of the west one-half of the northwest quarter of section 22, township 80, range 38, to be known as the town of Kirkman. The north and south streets, beginning on the west side of the railroad right of way, were named Madison street and Washington street. The east and west streets, beginning at the south side of the town, were Adams, Lincoln, State, Monroe, Van Buren and Congress…. A number of out-lots of the town of Kirkman were subsequently sub-divided and platted.
The town of Kirkman was incorporated on the 7th day of March, 1895. The first mayor of the town was J. M. Merritt and the firstbrecorder J. A. Hope. M. H. Woods was one of the first councilmen….
The post office of Kirkman was established on May 1, 1881, with J. W. French as postmaster.
When a federal census enumerator arrived at the Blaine’s Shelby County farm in June 1880, he noted that the household included farmer Lewis Blaine and his wife, Eliza, and their children Anna M., William E. and Sadie L. Blaine.
By 1895, there were still just one hundred and eighty-five people living in Kirkman. In 1900, the town’s residents included the following members of the Blaine family: family patriarch and matriarch Lewis and Eliza, and their daughters Nora Blaine and Anna M. (Blaine) Moler, a teacher in the Shelby County public schools who had married Thomas L. Moler on 6 March 1894, but had then been widowed by him when he passed away in Kirkman at the age of twenty-three on 24 August 1895.
In 1903, Lewis Blaine was given further sad news when he was notified that his older brother, William Allison Blaine, had died in Perry County, Pennsylvania on 5 February and had been buried at the Millerstown Riverview Cemetery in the Perry County community of Millerstown.
* Note: A veteran of the 208th Pennsylvania Volunteers, William A. Blaine (alternate surname spelling: “Blain”), had participated in the Union Army’s siege operations against the Virginia cities of Petersburg and Richmond in 1864 and 1865 prior to his hospitalization on 4 May 1865. Previously married to Mary Jones during the 1850s, he had welcomed the Perry County births of: Amanda T. Blaine (1858-1902), who had been born on 16 October 1858 and had later wed Captain Aaron Newton Buckman (1838-1916), who had served with the 3rd Pennsylvania Reserves during the American Civil War; Mary Josephine Blaine (1868-1943), who had been born on 30 October 1868; Nellie Gertrude Blaine (1874-1943), who had been born on 14 April 1874 and had later wed Anson Clarence White (1877-1964); James Durbin Blaine (1876-1931), who had been born on 5 October 1876; and William Ashley Blaine (1879-1958), who had been born on 14 March 1879 and had later wed Frances J. Snyder (1881-1967).
By 1905, the population of Lewis Blaine’s adopted hometown of Kirkman had grown to two hundred and twelve residents.
Illness, Death and Interment
Ailing with bowel issues, Lewis Blain underwent surgery at the hospital in Kirkman, Shelby County in January 1907, at the recommendation of his physician, but died following surgery. Just sixty-six years old at the time of his passing on 22 January 1907, he was interred at the Rose Hill Cemetery in Kirkman.
What Happened to Lewis Blaine’s Widow and Children?
Just over a month after Lewis Blaine’s death, his widow, Eliza (Smith) Blaine, applied for a U.S. Civil War Widow’s Pension, which was subsequently awarded. Still residing in Shelby County, Iowa as of the 1910 federal census, she was described by the enumerator that year as having her own income. Also residing with her were her daughter, Nora; and her eight-year-old granddaughter, Leta Woods, whose mother, Anna M. (Blaine Moler) Woods, had died from childbirth complications in 1904.
As happened with so many of her family members, Eliza (Smith) Blaine had a life that was all too short for those who loved her. Still in her mid-sixties at the time of her death in Kirkman in 1911, she was laid to rest beside her husband at the Rose Hill Cemetery in Kirkman.
Following the death of her first husband, Lewis and Eliza Blaine’s daughter, Anna M. (Blaine) Moler, returned to her parents’ home in Kirkman, Iowa. She then remarried circa 1901 — to James Woods. Two Shelby County-born children soon followed: Leta B. Woods (1902-1991), who was born on 16 January 1902 and later wed LeRoy Stanley Morgan (1899-1985); and Agnes Ann Woods (1904-1994), who was born on 6 March 1904 and later wed Harry Edwin Holmes (1902-1989) in 1923.
Tragically, the birth of that second daughter so severely weakened Anna (Blaine Moler) Woods that she died fourteen days later — on 20 March 1904, from childbirth-related complications. Following funeral services, she was laid to rest at Kirkman’s Rose Hill Cemetery. She was just thirty-two years old at the time of her passing. Her gravestone was inscribed with the following words:
Thy trials ended. Thy rest is won.
Following his marriage to Pearle Carter in Harlan, Iowa on 10 October 1900, Lewis Blaine’s son, William Edgar Blaine, welcomed the births of children: Vivian Blaine (1901-1996), who was born in Lake City, Calhoun County, Iowa on 8 November 1901 and later wed Richard A. Gaer (1901-1986) on 26 July 1922; Ercyle Edna Blaine (1903-2002), who was born in Carroll, Carroll County, Iowa on 4 February 1903 and later wed Clifford Ellis (1904-1981) on 13 February 1926; and Helen Pearle Blaine (1910-1974), who was born in Iowa in 1910 and later wed Ralph A. LeMoine (1906-1999) on 24 May 1930.
Long-time residents of Harlan, Iowa, William and Pearle Blaine made the decision, as they aged, to spend their winters in Cedar Falls, Iowa from 1955 through 1960, at which time they moved into the Cedar Falls Lutheran Home in January of 1960. Following his death from a heart attack there, at the age of eighty-three, on 4 February 1960, he was laid to rest at the Rose Hill Cemetery in Kirkman. He was survived by his daughters: Ercyle Edna (Blaine) Ellis, of Mapleton, Iowa; Vivian (Blaine) Gaer, of Cedar Falls; and Helen Pearl (Blaine) LeMoine of Waterloo, Iowa.
Following her marriage to Isaac Ferry, Lewis Blaine’s daughter, Sadi Lenore (Blaine) Ferry, who was known to family and friends as “Nora,” made her own life in Kirkman with her husband, who was known to family and friends as “Ike.” Sadly, their son, Lewis W. Ferry (1917-1917), died on the same day of his birth (12 February 1917). Unlike her sister, Nora survived and continued to reside with her husband until he widowed her in 1951. She then followed her husband in death in 1957. Following her passing at the age of seventy-eight in Kirkman on 11 February, she was also buried at Kirkman’s Rose Hill Cemetery.
What Happened to Lewis Blaine’s Other Siblings?
After marrying George Kochenderfer during the early 1860s, Josephine Ann (Blaine) Kochenderfer welcomed the births of children: Amos Jefferson Kochenderfer (1863-1936), who was born in Ickesberg, Perry County on 2 April 1863 and later wed Catherine E. Forsythe (1866-1939); Mary E. Kochenderfer (1865-1940), who was born on 9 September 1865 and later wed Robert Jackson Hartley (1865-1905); Harriet E. Kochenderfer (1869-1943), who was born in 1869 and later wed George Howard Cargill (1865-1928); John Philip Kochenderfer (1873-1936), who was born in Millerstown, Perry County on 11 August 1873 and later wed and was widowed by Laura Anna Hench (1878-1912), before marrying Florence A. Hoofnagle (1891-1946); Francis O. Kochenderfer (1875-1888), who was born in Oliver Township, Mifflin County on 2 July 1875, but died at the age of twelve in Mifflin County on 25 January 1888; and Naomi J. Kochenderfer (1878-1947), who was born in Millerstown on 1 January 1878 and later wed James Oscar Lewis (1874-1947).
After being widowed by George W. Kochenderfer in 1880, Josephine (Blaine) Kochenderfer married for a second time — in 1892 to Daniel Barrick (1827-1895). He then also widowed her when he passed away in Perry County on 29 January 1895. She survived her second husband by fifteen years. Following her death in Granville, Mifflin County, she was laid to rest at the Mattawana Cemetery in McVeytown, Mifflin County.
Jasper Harvey Blaine (1845-1930), who had been wounded in action in 1862, while serving with the 208th Pennsylvania Volunteers during the Civil War. Subsequently married to widow Sophia (Farmer) Sheeley (1845-1923) in Poweshiek County, Iowa on 21 November 1868, he then welcomed the births with her of: James Ulysses Blaine (1869-1960), who was born in Poweshiek County in 1869, was known to family and friends as “Jim” and later became a mail deliveryman and husband of Stella McConaughey (1873-1940); Cary Alden Blaine (1872-1959), who was born in Norway, Benton County, Iowa on 16 March 1872 and later wed Violet May Landon (1879-1978); and Cora Belle Blaine (1882-1901), who was born on 4 April 1882.
Residents of Douglas Township, Shelby County during the 1880s, 1890s and early 1900s, with the household made up of the Blaine family patriarch and matriarch and various combinations of their children at different times, according to federal census records, Jasper H. Blain and his family were farmers.
Between 1910 and 1923, he and his wife Sophia were “empty nesters” at their Shelby County farm. Sometime after his wife widowed him on 27 February 1923, he relocated to Oklahoma, took up farming there and then remarried — to Mrs. Ella (Fretz) Oliver (1861-1937) in Oklahoma County on 13 December 1924. By 1930, he and his second wife were documented by a federal census enumerator as residents of Edmond Township in Oklahoma County.
After a long, full life, Lewis Blaine’s brother, Captain Jasper Harvey Blaine answered his own final bugle call in Edmond, Oklahoma on 20 September 1930. Eighty-five years old at the time of his passing, he was laid to rest at the Memorial Park Cemetery in Oklahoma City.
Sources:
- Bates, Samuel P. History of Pennsylvania Volunteers, 1861-5, vol. 1. Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: B. Singerly, State Printer, 1869.
- Blain [sic, Blaine], Jasper H. (a brother of Lewis Blaine), Sophia, James, Samuel, and Cary (sons); and Sheley [sic, Sheeley], Lisbon (Sophia (Farmer Sheeley) Blaine’s son from her first marriage), in U.S. Census (Douglas Township, Shelby County, Iowa, 1880). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Blaine, Jasper H. (a brother of Lewis Blaine), Sophia, Cary, and Cora Bell [sic, Belle], in U.S. Census (Douglas Township, Shelby County, Iowa, 1900). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Blaine, Jasper H. (a brother of Lewis Blaine) and Sophia, in U.S. Census (Douglas Township, Shelby County, Iowa, 1910, 1920). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Blaine, Jasper H. (a brother of Lewis Blaine) and Ella, in U.S. Census (Edmond Township, Oklahoma County, Oklahoma, 1930). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Blain [sic, Blaine], Lewis, in Civil War Muster Rolls (Company D, 47th Pennsylvania Infantry). Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania State Archives.
- Blain [sic, Blaine], Lewis, in Civil War Veterans’ Card File, 1861-1866 (Company D, 47th Pennsylvania Infantry). Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania State Archives.
- Blain [sic, Blaine], Lewis, in Death and Burial Records (Shelby County, Iowa, 1907). Des Moines, Iowa: Iowa State Board of Health.
- Blain [sic, Blaine], Lewis, Eliza, Anna M., Wm. E., and Sadie L., in U.S. Census (Douglas Township, Shelby County, Iowa, 1880). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Blaine, Elisa and LeNora [sic, Eliza and Lenore/Nora] (mother and daughter); and Woods, Lydia [sic, Leta], in U.S. Census (Douglas Township, Shelby County, Iowa, 1910). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Blaine, Lewis and Eliza, in U.S. Civil War Pension General Index Cards (veteran’s application no.: 135147, certificate no.: 221931, filed from Pennsylvania by the veteran, 24 August 1868; widow’s application no.: 864929, certificate no.: 645092, filed by the veteran’s widow, Eliza Blaine, from Iowa, 12 March 1907). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- Blane [sic, Blaine], Lewis, Eliza and Nora; and Moler, Anna M. (Nora Blaine’s widowed sister). Washington, D.C.: U.S. National Archives and Records Administration.
- “Capt. J. H. Blaine Laid to Rest” (obituary of Lewis W. Blaine’s brother, Jasper Harvey Blaine). Edmond, Oklahoma: Edmond Enterprise, 25 September 1930.
- Ercyle Edna Blaine (daughter), William Edgar Blaine (father) and Pearle E. Carter (mother), in Birth Records (Carroll County, Iowa, 1903). Des Moines, Iowa: Iowa State Board of Health.
- “Florida’s Role in the Civil War,” in Florida Memory. Tallahassee, Florida: State Archives of Florida.
- Hain, Harry Harrison. History of Perry County, Pennsylvania. Including Descriptions of Indians and Pioneer Life from the Time of Earliest Settlement. Harrisburg, Pennsylvania: Hain-Moore Company, 1922.
- Jasper H. Blaine (groom and a brother of Lewis Blaine), and Sophia Seeley (bride), in Marriage Records (Poweshiek County, Iowa, 1868). Des Moines, Iowa: Iowa State Board of Health.
- Jasper Harvey Blaine (groom and a brother of Lewis Blaine), and Ella Oliver (bride), in Marriage Records (Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, 1924). Oklahoma City, Oklahoma: Oklahoma Historical Socirty.
- “Lewis Blain” [sic, Blaine] (obituary). Newport, Pennsylvania: The News, 31 January 1907.
- “Roster of the 47th P. V. Inf.” Allentown, Pennsylvania: The Morning Call, 26 October 1930.
- Schmidt, Lewis. A Civil War History of the 47th Regiment of Pennsylvania Veteran Volunteers. Allentown, Pennsylvania: Self-published, 1986.
- “The History of the Forty-Seventh Regt. P. V.” Allentown, Pennsylvania: The Lehigh Register, 20 July 1870.
- Thomas M. Moler (groom) and Anna M. Blaine (bride), in “Return of Marriages in the County of Shelby” (1894). Des Moines, Iowa: Iowa State Board of Health.
- “Veteran of Civil War Passes Away at Edmond” (obituary of Jasper Harvey Blaine, a brother of Lewis Blaine). Jones, Oklahoma: The Oklahoma County News, 3 October 1930.
- Vivian L. Blaine (daughter), William Edgar Blaine (father) and Pearle E. Carter (mother), in Birth Records (Calhoun County, Iowa, 1901). Des Moines, Iowa: Iowa State Board of Health.
- “Vivian L. Gaer” (obituary of a granddaughter of Lewis Blaine), in “Metro Deaths.” Waterloo, Iowa: Waterloo-Cedar Falls Courier, 20 February 1996.
- White, Edward S. Past and Present of Shelby County Iowa, vol. 1. Indianapolis, Indiana: B. F. Bowen & Company, Inc., 1915.
- “William E. Blaine” (obituary). Waterloo, Iowa: Waterloo Daily Courier, 5 February 1960.








You must be logged in to post a comment.